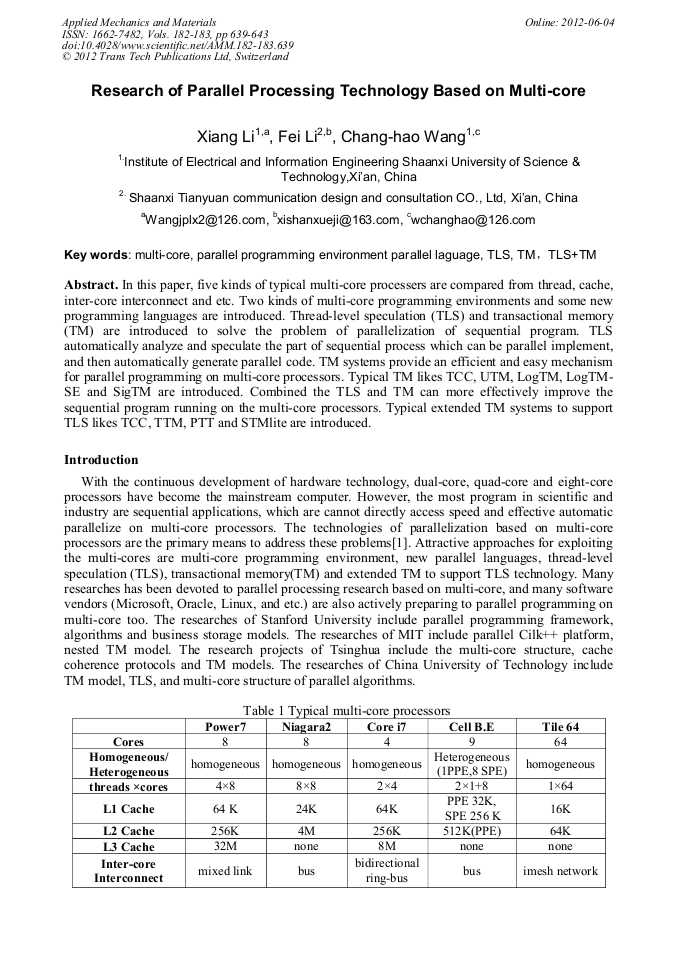
[1]
C. Hughes and T. Hughes, Professional Multicore Programming Design and Implementation for C++ Developer, Wrox, United Kingdom, 2008, pp.15-50.
Google Scholar
[2]
G.P. Long, J.C. Zhang, and D.R. Fan, Architectural Support and Evaluation of Cilk Language on Many-Core Architectures, Chinese Journal of Computers, China, 2008, vol. 31, p.1975-(1985).
DOI: 10.3724/sp.j.1016.2008.01975
Google Scholar
[3]
A. D. Stefano, and C. Santoro, Using the Erlang Language for Multi-agent Systems Implementation, International Conference on Intelligent Agent Technology, 2005, pp.679-685.
DOI: 10.1109/iat.2005.141
Google Scholar
[4]
M. J. Bridges, The Velocity Compiler: Efficient Multicore Execution From Legacy Sequential Codes, Princeton University, USA, 2008, pp.7-30.
Google Scholar
[5]
C. E. Oancea ,A. Mycroft, and T. Harris, A lightweight In-place Implementation for Software Thread-level Speculation, " SPAA, 09, Canada, 2009, pp.223-232.
DOI: 10.1145/1583991.1584050
Google Scholar
[6]
K. Olukotun, L. Hammond, and J. Laudon, Chip Multiprocessor Architecture: Techniques to Improve Throughput and Latency, Morgan and Claypool Publishers, USA, 2009, pp.61-136.
DOI: 10.1007/978-3-031-01720-9_3
Google Scholar
[7]
T. Chen, Speculative Parallelization on Multicore Processors, University of California, Riverside, USA, 2010, pp.72-148.
Google Scholar
[8]
L. Peng, L. Xie, and X. Zhang, Transactional Memory System, Journal of Computer Research and Development, China, 2009, 46, vol. 8, pp.1386-1398.
Google Scholar
[9]
L. Hammond, V. Wong, M. Chen, and et al., Transactional Memory Coherence and Consistency, " ISCA , 04, ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, Vo. 32, USA, 2004, pp.102-113.
DOI: 10.1145/1028176.1006711
Google Scholar
[10]
C. S. Ananian, K. Asanovi, B. C. Kuszmaul, C. E. Leiserson, and S. Lie, Unbounded Transactional Memory, IEEE Micro, Vol. 26 USA, 2006, pp.59-69.
DOI: 10.1109/mm.2006.26
Google Scholar
[11]
M. Nasir. Software Transactional Memory Techniques Principles, Design, and Implementation Trade-offs, School of Computing Blekinge Institute of Technology, Sweden, 2009, PP. 14-62.
Google Scholar
[12]
B. Saha, A. R. Adl-Tabatabai, R. L. Hudson, C. C. Minh and B. Hertzberg, McRT-STM: a High Performance Software Transactional Memory System for a Multi-core Runtime, 11th ACM SIGPLAN Symposium on Principles and Practice of Parallel Programming, USA, 2006, p.187.
DOI: 10.1145/1122971.1123001
Google Scholar
[13]
R. Rajwar, M. Herlihy and K. Lai, Virtualizing Transactional Memory, ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, Vo. 33, USA, 2005, pp.494-505.
DOI: 10.1145/1080695.1070011
Google Scholar
[14]
P. Damron, A. Fedorova, Y. Lev, and et al., Hybrid Transactional Memory, International Conference on Architectural Support for Programming Languages and Operating Systems, (2006).
DOI: 10.1145/1168857.1168900
Google Scholar
[15]
M. M. Swift, H. Volos, N. Goyal, L. Yen, M. D. Hill and D. A. Wood, OS Support for Virtualizing Hardware Transactional Memory, TRANSACTS 3, (2008).
Google Scholar
[16]
C. C. Minh, M. Trautmann, J. W. Chung, A. McDonald, N. Bronson, J. Casper, C. Kozyrakis and K. Olukotun, An Effective Hybrid Transactional Memory System with Strong Isolation Guarantees, Sigarch Compute, vol. 35, USA, 2007, p.69–80.
DOI: 10.1145/1273440.1250673
Google Scholar
[17]
R. M. Yoo, H.H.S. Lee, Helper Transactions: Enabling Thread-Level Speculation via a Transactional Memory System, PESPMA 2008, pp.63-71.
Google Scholar
[18]
K. E. Moore, M. D. Hill and D. A. Wood, Thread-Level Transactional Memory, Technical Report 1524, Computer Sciences UW-Madison, (2005).
Google Scholar
[19]
Y.B. Wang, Performance Optimization on Multicore Transactional Memory Architecture Supporting Speculative Parallelization, University of Science and Technology of China, China 2010, pp.10-90.
Google Scholar
[20]
M. Mehrara, J. Hao, P.C. Hsu, and S. Mahlke, Parallelizing Sequential Applications on Commodity Hardware using a Low-cost Software Transactional Memory, " PLDI, 09, Dublin, 2009, pp.166-176.
DOI: 10.1145/1543135.1542495
Google Scholar