p.839
p.843
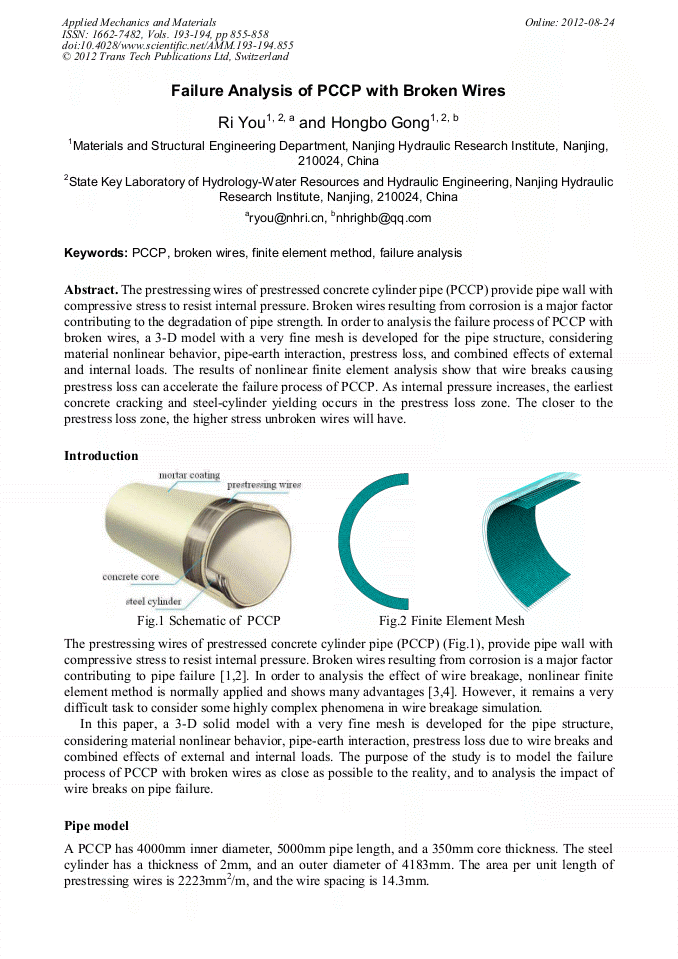
p.847
p.852
p.855
p.859
p.864
p.868
p.872
Failure Analysis of PCCP with Broken Wires
Abstract:
The prestressing wires of prestressed concrete cylinder pipe (PCCP) provide pipe wall with compressive stress to resist internal pressure. Broken wires resulting from corrosion is a major factor contributing to the degradation of pipe strength. In order to analysis the failure process of PCCP with broken wires, a 3-D model with a very fine mesh is developed for the pipe structure, considering material nonlinear behavior, pipe-earth interaction, prestress loss, and combined effects of external and internal loads. The results of nonlinear finite element analysis show that wire breaks causing prestress loss can accelerate the failure process of PCCP. As internal pressure increases, the earliest concrete cracking and steel-cylinder yielding occurs in the prestress loss zone. The closer to the prestress loss zone, the higher stress unbroken wires will have.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
855-858
Citation:
Online since:
August 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: