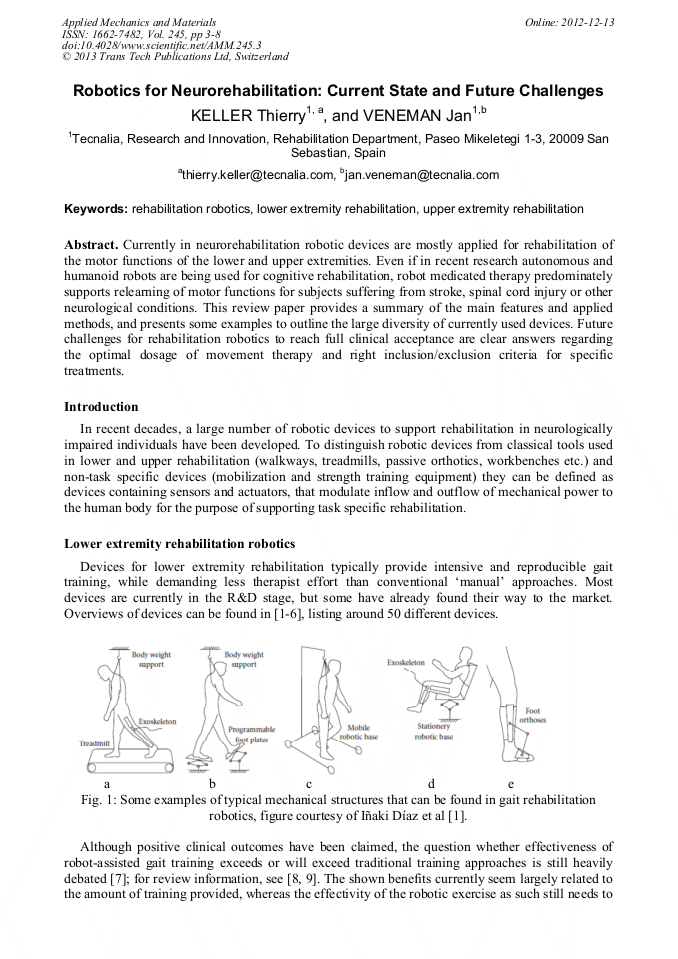
[1]
I.Díaz I, J.J. Gil JJ, E. Sánchez, Lower-Limb Robotic Rehabilitation. Literature Review and Challenges, Article ID 759764, Journal of Robotics, (2011).
DOI: 10.1155/2011/759764
Google Scholar
[2]
Hesse S, Werner C, Seibel H, von Frankenberg S, Kappel EM, Kirker S, Käding M.Treadmill training with partial body-weight support after total hip arthroplasty: a randomized controlled trial, Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 84(12) (2003) 1767-73.
DOI: 10.1016/s0003-9993(03)00434-9
Google Scholar
[3]
D.P. Ferris, J.M. Czerniecki, B.Hannaford, An ankle-foot orthosis powered by artificial pneumatic muscles, J Appl Biomech 21(2) (2005) 189-97.
DOI: 10.1123/jab.21.2.189
Google Scholar
[4]
S.P. Messier, R.F. Loeser, J.L. Hoover, Semble EL, C.M. Wise, Osteoarthritis of the knee: effects on gait, strength, and flexibility, Archives of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation 73(1) (1992) 29–36.
Google Scholar
[5]
C. Senanayake, S.M.N.A. Senanayake, Emerging robotics devices for therapeutic rehabilitation of the lower extremity, Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, IEEE/ASME International Conference, 2009.
DOI: 10.1109/aim.2009.5229740
Google Scholar
[6]
S. Hussain, S. Xie, G. Liu, Robot assisted treadmill training: Mechanisms and training strategies, Med Eng Phys 33(5) (2011) 527-33.
DOI: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2010.12.010
Google Scholar
[7]
B.H. Dobkin, P.W. Duncan, Should body weight-supported treadmill training and robotic-assistive steppers for locomotor training trot back to the starting gate?, Neurorehabil Neural Repair 26(4) (2012) 308-17.
DOI: 10.1177/1545968312439687
Google Scholar
[8]
C. Tefertiller, B. Pharo, N. Evans, P. Winchester, Efficacy of rehabilitation robotics for walking training in neurological disorders: a review, J Rehabil Res Dev. 48(4) (2011) 387-416.
DOI: 10.1682/jrrd.2010.04.0055
Google Scholar
[9]
J. Mehrholz, R. Friis, J. Kugler, S. Twork, A. Storch, Pohl M.Treadmill training for patients with Parkinson's disease, Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 20 (2010) 1pp.
DOI: 10.1002/14651858.cd007830.pub2
Google Scholar
[10]
L. Marchal-Crespo, D.M. Reinkensmeyer, Review of control strategies for robotic movement training after neurologic injury, J Neuroeng Rehabil. (2009) 6-20.
DOI: 10.1186/1743-0003-6-20
Google Scholar
[11]
J. F. Veneman, R. Ekkelenkamp, R. Kruidhof, F. C.T. van der Helm, H. van der Kooij, A Series elastic- and bowden-cable-based actuation system for use as torque actuator in exoskeleton-type robots, International Journal of Robotics Research 25 (2006) 261-281.
DOI: 10.1177/0278364906063829
Google Scholar
[12]
P. Langhorne, F. Coupar, A. Pollock, Motor recovery after stroke: a systematic review, Lancet Neurol. 8(8) (2009) 741-54.
DOI: 10.1016/s1474-4422(09)70150-4
Google Scholar
[13]
J. Klein, S.J. Spencer, D.J. Reinkensmeyer, Breaking it down is better: haptic decomposition of complex movements aids in robot-assisted motor learning, IEEE Trans Neural Syst Rehabil Eng 20(3) (2012) 268-75.
DOI: 10.1109/tnsre.2012.2195202
Google Scholar
[14]
S. Hesse, C. Werner, M. Pohl, S. Rueckriem, J. Mehrholz, M.L. Lingnau, Computerized arm training improves the motor control of the severely affected arm after stroke: a single-blinded randomized trial in two centers, Stroke 36(9) (2005) 1960-1966.
DOI: 10.1161/01.str.0000177865.37334.ce
Google Scholar
[15]
C.D. Takahashi, L. Der-Yeghiaian , V. Le, R.R. Motiwala, S.C. Cramer, Robot-based hand motor therapy after stroke, Brain 131(2008) 425-37.
DOI: 10.1093/brain/awm311
Google Scholar
[16]
N. Hogan, H.I. Krebs, B. Rohrer, J.J. Palazzolo, L. Dipietro, S.E. Fasoli, J. Stein, R. Hughes, W.R. Frontera, D. Lynch, B.T. Volpe, Motions or muscles? Some behavioral factors underlying robotic assistance of motor recovery, J Rehabil Res Dev. 43(5) (2006) 605-18.
DOI: 10.1682/jrrd.2005.06.0103
Google Scholar
[17]
J.L. Patton, M.E. Stoykov, M. Kovic, F.A. Mussa-Ivaldi, Evaluation of robotic training forces that either enhance or reduce error in chronic hemiparetic stroke survivors, Exp Brain Res. 168(3) (2006) 368-83.
DOI: 10.1007/s00221-005-0097-8
Google Scholar
[18]
J.C. Perry, J. Andureu, F.I. Cavallaro, J.F. Veneman, S.P. Carmien T. Keller, Effective game use in neurorehabilitation: user-centered perspectives, in Handbook of Research on Improving Learning and Motivation through Educational Games, IGI Global, (2011) 683-725.
DOI: 10.4018/978-1-60960-495-0.ch032
Google Scholar
[19]
B.R. Brewer, S.K McDowell., L.C. Worthen-Chaudhari, Poststroke upper extremity reha-bilitation: a review of robotic systems and clinical results, Top Stroke Rehabil. 14(6) (2007) 22-44.
DOI: 10.1310/tsr1406-22
Google Scholar
[20]
I. Sarakoglou, S. Kousidou, N. Tsagarakis and D.G. Caldwell, Exoskeleton-Based Exercisers for the Disabilities of the Upper Arm and Hand, In Rehabilitation Robotics, S.S. Kommu, Ed., InTech, Vienna, Austria, (2007) 499-522.
DOI: 10.5772/5177
Google Scholar
[21]
A.C. Lo, P.D. Guarino, L.G. Richards, et. al., Robot-Assisted Therapy for Long-Term Upper-Limb Impairment after Stroke, N Engl J Med 362 (2010) 1772-1783.
Google Scholar