p.2356
p.2361
p.2367
p.2371
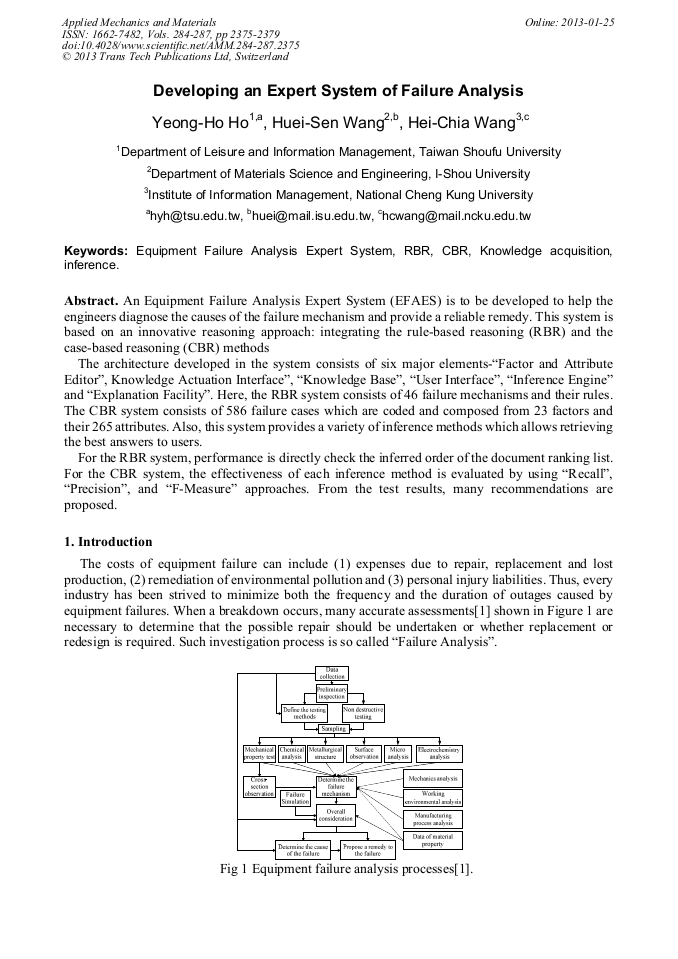
p.2375
p.2380
p.2385
p.2391
p.2396
Developing an Expert System of Failure Analysis
Abstract:
An Equipment Failure Analysis Expert System (EFAES) is to be developed to help the engineers diagnose the causes of the failure mechanism and provide a reliable remedy. This system is based on an innovative reasoning approach: integrating the rule-based reasoning (RBR) and the case-based reasoning (CBR) methods The architecture developed in the system consists of six major elements-“Factor and Attribute Editor”, Knowledge Actuation Interface”, “Knowledge Base”, “User Interface”, “Inference Engine” and “Explanation Facility”. Here, the RBR system consists of 46 failure mechanisms and their rules. The CBR system consists of 586 failure cases which are coded and composed from 23 factors and their 265 attributes. Also, this system provides a variety of inference methods which allows retrieving the best answers to users. For the RBR system, performance is directly check the inferred order of the document ranking list. For the CBR system, the effectiveness of each inference method is evaluated by using “Recall”, “Precision”, and “F-Measure” approaches. From the test results, many recommendations are proposed.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2375-2379
Citation:
Online since:
January 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: