p.1813
p.1818
p.1822
p.1826
p.1834
p.1840
p.1845
p.1851
p.1856
Experimental Study on the Reverse Cleaning and Regeneration of Diesel Engine's Metal Mesh Filter
Abstract:
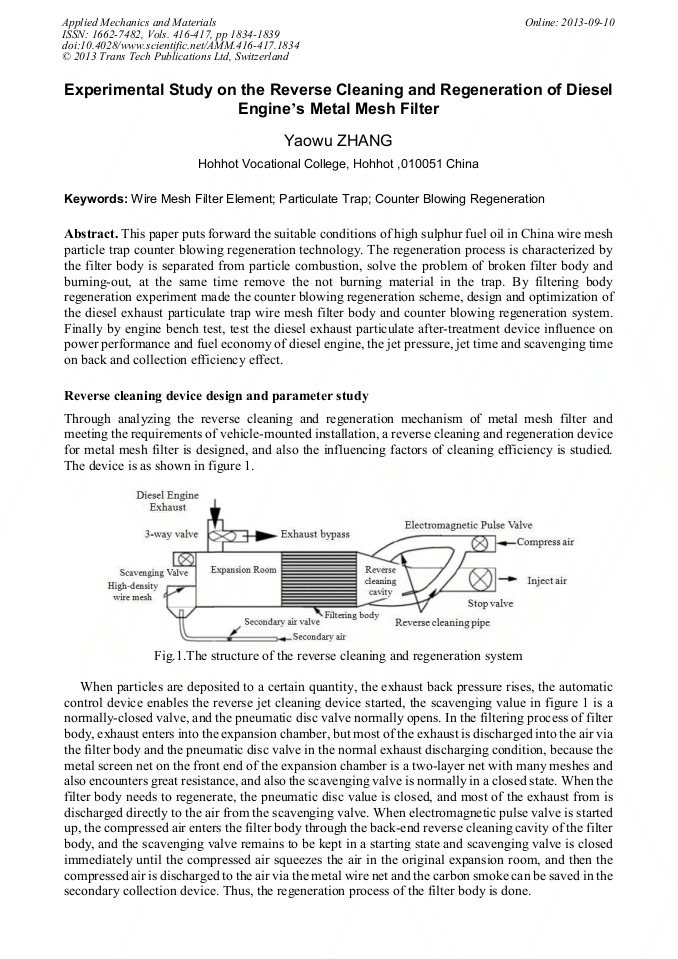
This paper puts forward the suitable conditions of high sulphur fuel oil in China wire mesh particle trap counter blowing regeneration technology. The regeneration process is characterized by the filter body is separated from particle combustion, solve the problem of broken filter body and burning-out, at the same time remove the not burning material in the trap. By filtering body regeneration experiment made the counter blowing regeneration scheme, design and optimization of the diesel exhaust particulate trap wire mesh filter body and counter blowing regeneration system. Finally by engine bench test, test the diesel exhaust particulate after-treatment device influence on power performance and fuel economy of diesel engine, the jet pressure, jet time and scavenging time on back and collection efficiency effect.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1834-1839
Citation:
Online since:
September 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: