p.2188
p.2192
p.2196
p.2200
p.2204
p.2208
p.2216
p.2220
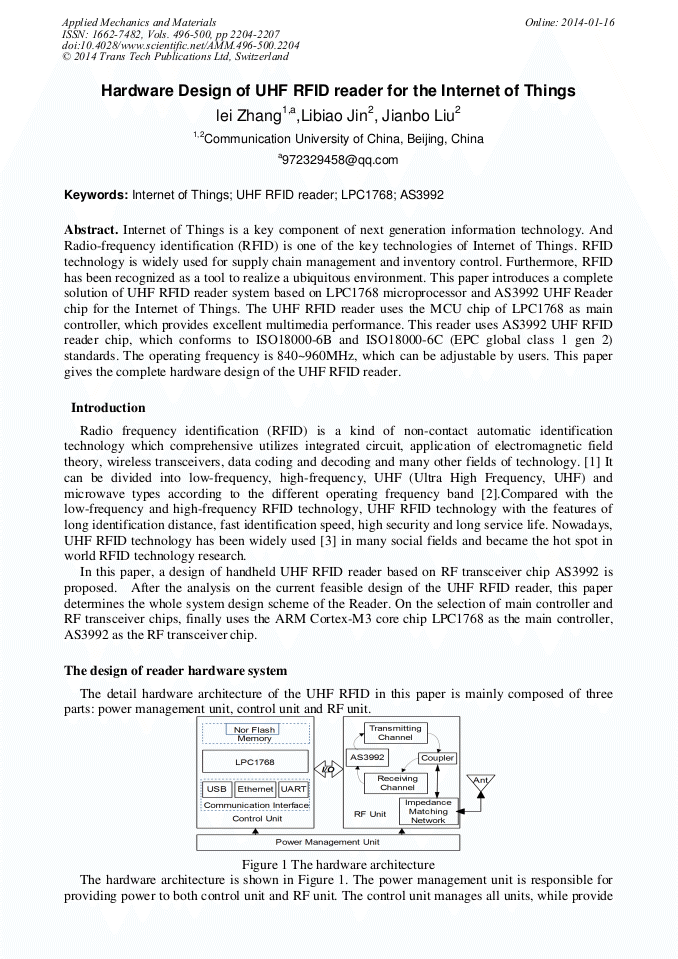
p.2224
Hardware Design of UHF RFID Reader for the Internet of Things
Abstract:
Internet of Things is a key component of next generation information technology. And Radio-frequency identification (RFID) is one of the key technologies of Internet of Things. RFID technology is widely used for supply chain management and inventory control. Furthermore, RFID has been recognized as a tool to realize a ubiquitous environment. This paper introduces a complete solution of UHF RFID reader system based on LPC1768 microprocessor and AS3992 UHF Reader chip for the Internet of Things. The UHF RFID reader uses the MCU chip of LPC1768 as main controller, which provides excellent multimedia performance. This reader uses AS3992 UHF RFID reader chip, which conforms to ISO18000-6B and ISO18000-6C (EPC global class 1 gen 2) standards. The operating frequency is 840~960MHz, which can be adjustable by users. This paper gives the complete hardware design of the UHF RFID reader.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2204-2207
Citation:
Online since:
January 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: