p.1009
p.1013
p.1017
p.1021
p.1026
p.1030
p.1034
p.1038
p.1042
Study on Processing Technology of Turbocharger Impeller and Shaft
Abstract:
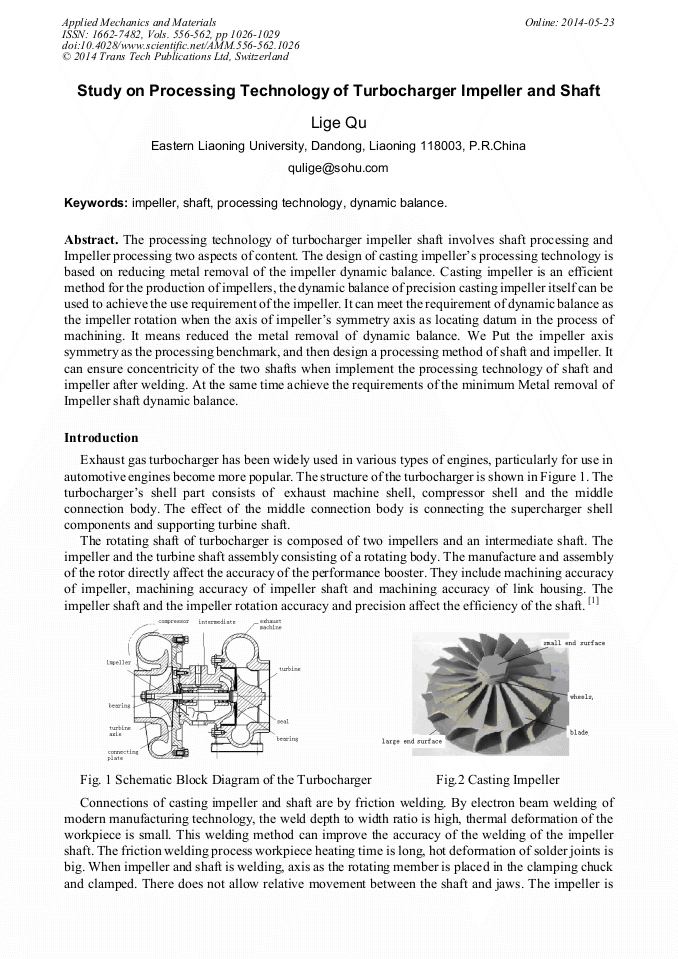
The processing technology of turbocharger impeller shaft involves shaft processing and Impeller processing two aspects of content. The design of casting impeller’s processing technology is based on reducing metal removal of the impeller dynamic balance. Casting impeller is an efficient method for the production of impellers, the dynamic balance of precision casting impeller itself can be used to achieve the use requirement of the impeller. It can meet the requirement of dynamic balance as the impeller rotation when the axis of impeller’s symmetry axis as locating datum in the process of machining. It means reduced the metal removal of dynamic balance. We Put the impeller axis symmetry as the processing benchmark, and then design a processing method of shaft and impeller. It can ensure concentricity of the two shafts when implement the processing technology of shaft and impeller after welding. At the same time achieve the requirements of the minimum Metal removal of Impeller shaft dynamic balance.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1026-1029
Citation:
Online since:
May 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: