p.1084
p.1089
p.1094
p.1099
p.1104
p.1109
p.1114
p.1119
p.1125
Low Cycle Fatigue Analysis of after Treatment Device Induced due to Thermal Load by Using Finite Element Analysis
Abstract:
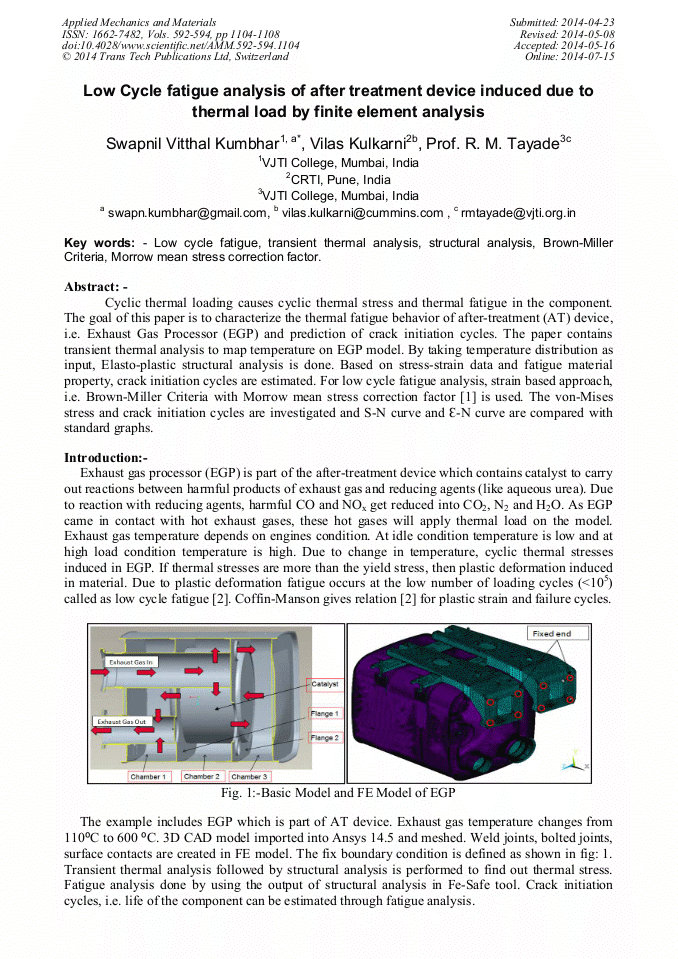
Cyclic thermal loading causes cyclic thermal stress and thermal fatigue in the component. The goal of this paper is to characterize the thermal fatigue behavior of after-treatment (AT) device, i.e. Exhaust Gas Processor (EGP) and prediction of crack initiation cycles. The paper contains transient thermal analysis to map temperature on EGP model. By taking temperature distribution as input, Elasto-plastic structural analysis is done. Based on stress-strain data and fatigue material property, crack initiation cycles are estimated. For low cycle fatigue analysis, strain based approach, i.e. Brown-Miller Criteria with Morrow mean stress correction factor [1] is used. The von-Mises stress and crack initiation cycles are investigated and S-N curve and Ɛ-N curve are compared with standard graphs.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1104-1108
Citation:
Online since:
July 2014
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: