p.46
p.52
p.60
p.65
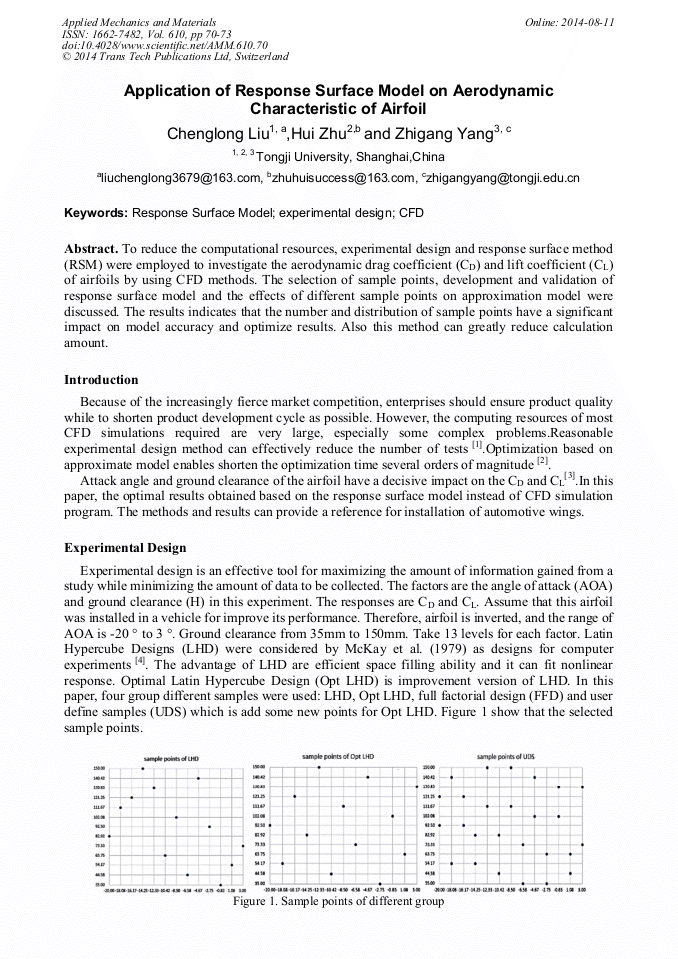
p.70
p.74
p.78
p.84
p.88
Application of Response Surface Model on Aerodynamic Characteristic of Airfoil
Abstract:
To reduce the computational resources, experimental design and response surface method (RSM) were employed to investigate the aerodynamic drag coefficient (CD) and lift coefficient (CL) of airfoils by using CFD methods. The selection of sample points, development and validation of response surface model and the effects of different sample points on approximation model were discussed. The results indicates that the number and distribution of sample points have a significant impact on model accuracy and optimize results. Also this method can greatly reduce calculation amount.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
70-73
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
August 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: