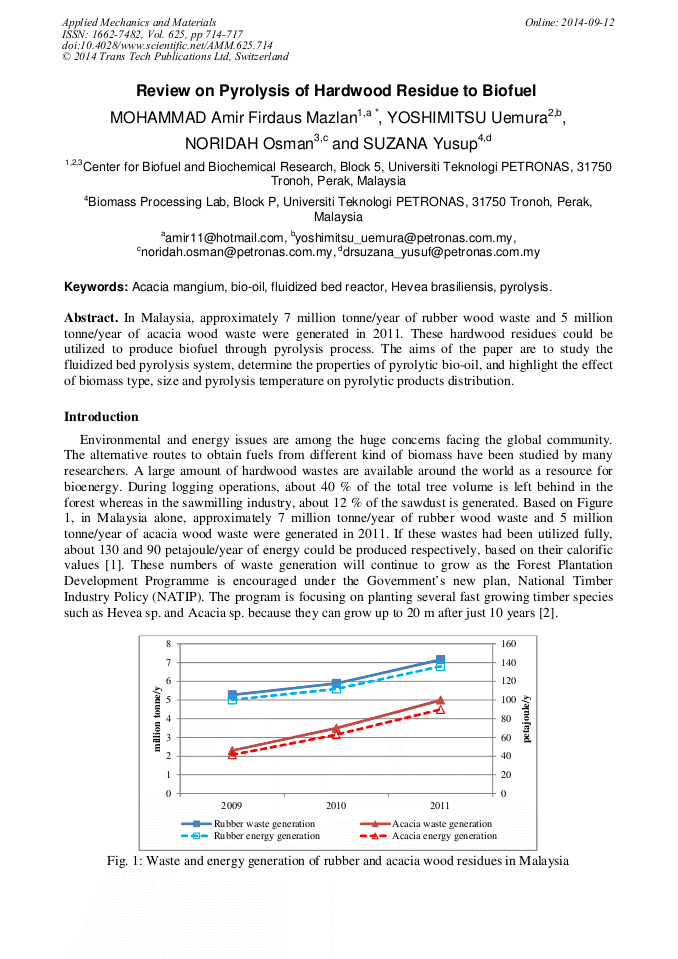
[1]
MTIB, Malaysian Timber Statistics 2009-2011, Malaysian Timber Industry Board (2012).
Google Scholar
[2]
FPD, Forest Plantation, Forest Plantation Development Sdn Bhd (2010).
Google Scholar
[3]
M.V.D. Velden, J. Baeyans, B. Janssens, R. Dewil, Fundamentals, kinetics and endothermicity of the biomass pyrolysis reaction, Renewable Energy 35 (2010) 232-242.
DOI: 10.1016/j.renene.2009.04.019
Google Scholar
[4]
A.V. Bridgwater, Review of fast pyrolysis of biomass and product upgrading, Biomass Bioenergy 38 (2012) 68-94.
DOI: 10.1016/j.biombioe.2011.01.048
Google Scholar
[5]
J. Lehto, Y. Solantausta, M. Kytö, D. Chiaramonti, Review of fuel oil quality and combustion of fast pyrolysis bio-oils from lignocellulosic biomass, Applied Energy 116 (2014) 178-190.
DOI: 10.1016/j.apenergy.2013.11.040
Google Scholar
[6]
A. Oasmaa, C. Peacocke, A guide to physical property characterisation of biomass-derived fast pyrolysis liquids. VTT Publications (2010).
Google Scholar
[7]
D. Mohan, C.U. Pittman, P.H. Steele, Pyrolysis of wood/biomass for bio-oil: A critical review, Energy Fuels 20 (2006) 848-890.
DOI: 10.1021/ef0502397
Google Scholar
[8]
S. Czernik, A.V. Bridgwater, Overview of applications of biomass fast pyrolysis oil, Energy Fuels 18 (2004) 590-598.
DOI: 10.1021/ef034067u
Google Scholar
[9]
H.S. Heo, H.J. Park, C. Ryu, D.J. Suh, S.S. Kim, Bio-oil production from fast pyrolysis of waste furniture sawdust in a fluidized bed, Bioresoure Technology 101 (2010) 91-96.
DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2009.06.003
Google Scholar
[10]
Z.J. Lu, Y.K. Park, Pyrolysis oil from fast pyrolysis of maize stalk, Journal of Applied Pyrolysis 83 (2008) 206-212.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2008.08.005
Google Scholar
[11]
N. Ali, Effect of operating conditions and fractional condensation on pyrolytic products, Journal of the Japan Institute of Energy, 92 (2013) 1014-1020.
DOI: 10.3775/jie.92.1014
Google Scholar
[12]
S. Yaman, Pyrolysis of biomass to produce fuels and chemical feedstocks, Energy Conversion and Management 45 (2004) 651-671.
DOI: 10.1016/s0196-8904(03)00177-8
Google Scholar
[13]
K.G. Lim, R. Egashira, Pyrolysis and characterization of the products for recycle of rubberwood residues, Journal of Applied Sciences 5 (2005), 104-107.
Google Scholar
[14]
M. Amutio, G. Lopez, J. Alvarez, M. Olazar, J. Bilbao, Flash pyrolysis of forestry residues from the Portuguese Central Inland Region, Bioresource Technology 129 (2013) 512-518.
DOI: 10.1016/j.biortech.2012.11.114
Google Scholar
[15]
J. Shen, X.S. Wang, D. Mourant, M.J. Rhodes, Effects of particle size on the fast pyrolysis of oil mallee woody biomass, Fuel 88 (2009) 1810-1817.
DOI: 10.1016/j.fuel.2009.05.001
Google Scholar
[16]
S.S. Liaw, Z. Wang, P. Ndegwa, C. Frear, M.G. Perez, Effect of pyrolysis temperature on the yield and properties of bio-oils obtained from the auger pyrolysis of Douglas Fir wood, Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis 93 (2012) 52-62.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jaap.2011.09.011
Google Scholar