p.274
p.283
p.289
p.295
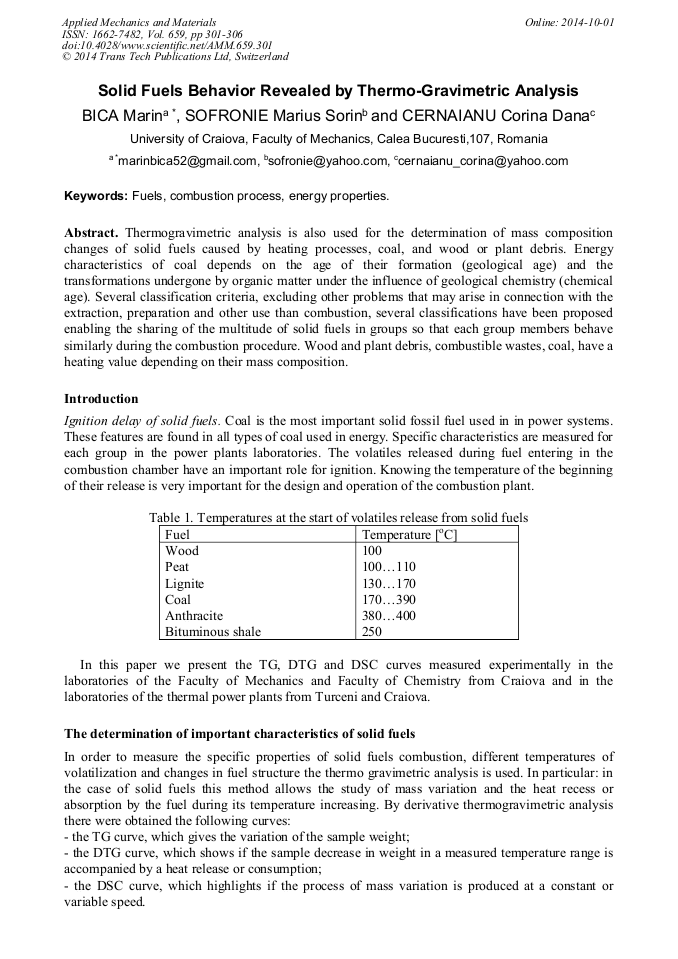
p.301
p.307
p.313
p.319
p.325
Solid Fuels Behavior Revealed by Thermo-Gravimetric Analysis
Abstract:
Thermogravimetric analysis is also used for the determination of mass composition changes of solid fuels caused by heating processes, coal, and wood or plant debris. Energy characteristics of coal depends on the age of their formation (geological age) and the transformations undergone by organic matter under the influence of geological chemistry (chemical age). Several classification criteria, excluding other problems that may arise in connection with the extraction, preparation and other use than combustion, several classifications have been proposed enabling the sharing of the multitude of solid fuels in groups so that each group members behave similarly during the combustion procedure. Wood and plant debris, combustible wastes, coal, have a heating value depending on their mass composition.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
301-306
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
October 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: