p.128
p.133
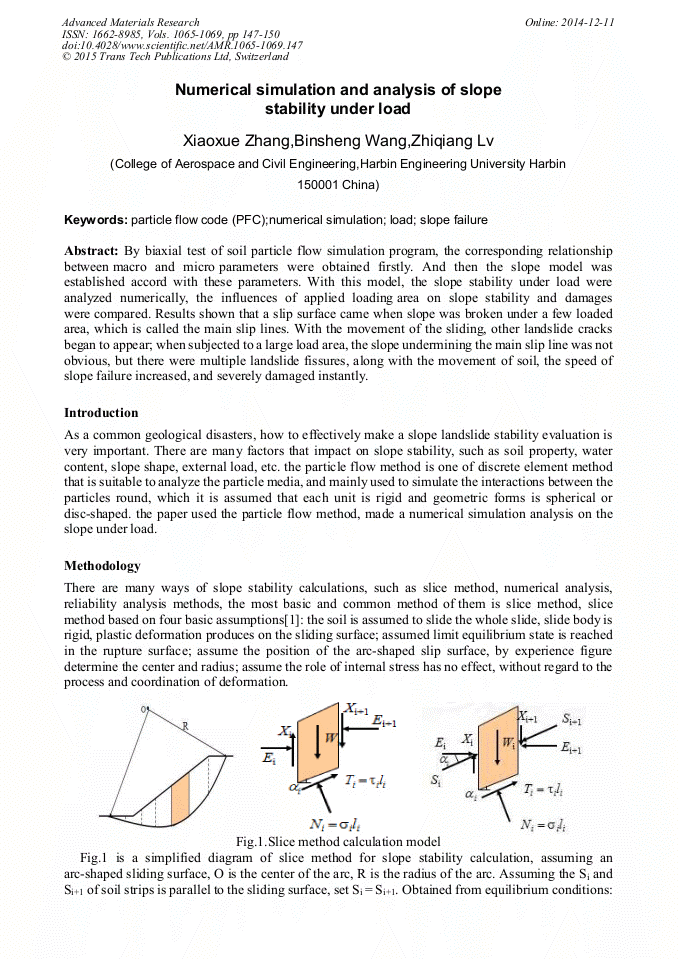
p.138
p.143
p.147
p.151
p.159
p.164
p.168
Numerical Simulation and Analysis of Slope Stability under Load
Abstract:
By biaxial test of soil particle flow simulation program, the corresponding relationship between macro and micro parameters were obtained firstly. And then the slope model was established accord with these parameters. With this model, the slope stability under load were analyzed numerically, the influences of applied loading area on slope stability and damages were compared. Results shown that a slip surface came when slope was broken under a few loaded area, which is called the main slip lines. With the movement of the sliding, other landslide cracks began to appear; when subjected to a large load area, the slope undermining the main slip line was not obvious, but there were multiple landslide fissures, along with the movement of soil, the speed of slope failure increased, and severely damaged instantly.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
147-150
Citation:
Online since:
December 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2015 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: