p.613
p.617
p.622
p.628
p.632
p.636
p.640
p.644
p.648
Sensorless Parameter Identification Method for PMSM Based on Double Manifold Sliding Mode
Abstract:
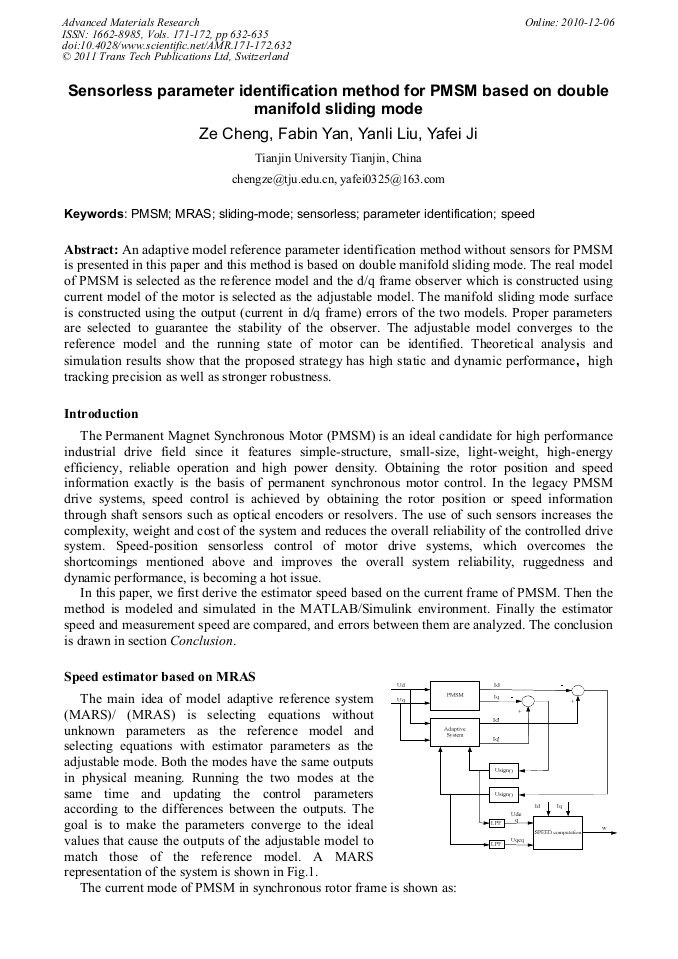
An adaptive model reference parameter identification method without sensors for PMSM is presented in this paper and this method is based on double manifold sliding mode. The real model of PMSM is selected as the reference model and the d/q frame observer which is constructed using current model of the motor is selected as the adjustable model. The manifold sliding mode surface is constructed using the output (current in d/q frame) errors of the two models. Proper parameters are selected to guarantee the stability of the observer. The adjustable model converges to the reference model and the running state of motor can be identified. Theoretical analysis and simulation results show that the proposed strategy has high static and dynamic performance,high tracking precision as well as stronger robustness.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
632-635
Citation:
Online since:
December 2010
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: