p.909
p.915
p.919
p.925
p.930
p.937
p.942
p.947
p.951
Numerical Simulation of Gas Flow Field in the Moving Bed of Corex Melter-Gasifier
Abstract:
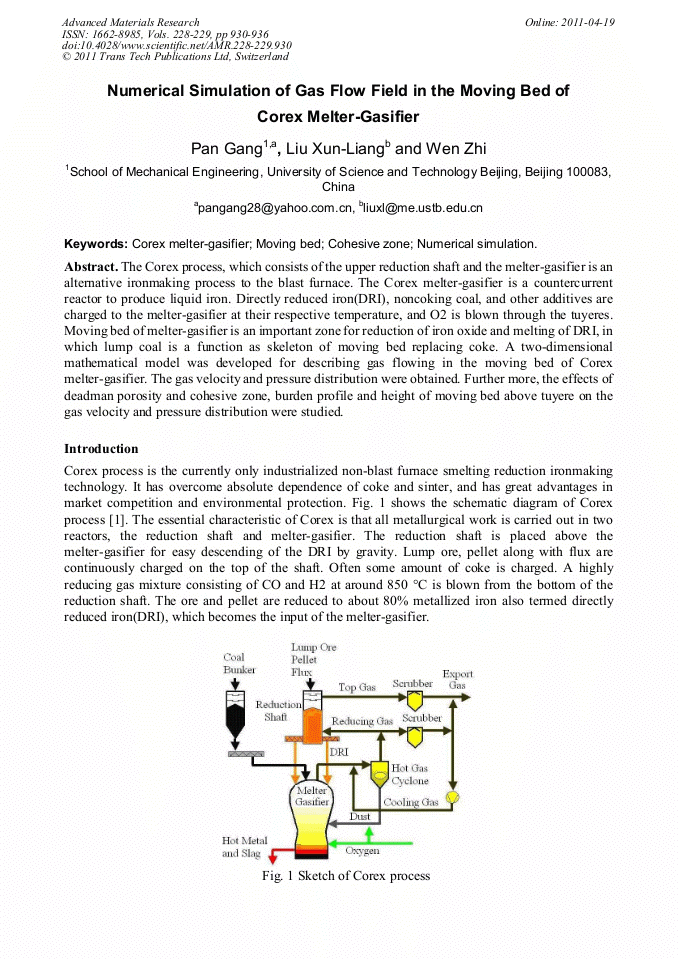
The Corex process, which consists of the upper reduction shaft and the melter-gasifier is an alternative ironmaking process to the blast furnace. The Corex melter-gasifier is a countercurrent reactor to produce liquid iron. Directly reduced iron(DRI), noncoking coal, and other additives are charged to the melter-gasifier at their respective temperature, and O2 is blown through the tuyeres. Moving bed of melter-gasifier is an important zone for reduction of iron oxide and melting of DRI, in which lump coal is a function as skeleton of moving bed replacing coke. A two-dimensional mathematical model was developed for describing gas flowing in the moving bed of Corex melter-gasifier. The gas velocity and pressure distribution were obtained. Further more, the effects of deadman porosity and cohesive zone, burden profile and height of moving bed above tuyere on the gas velocity and pressure distribution were studied.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
930-936
Citation:
Online since:
April 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: