p.3233
p.3241
p.3245
p.3250
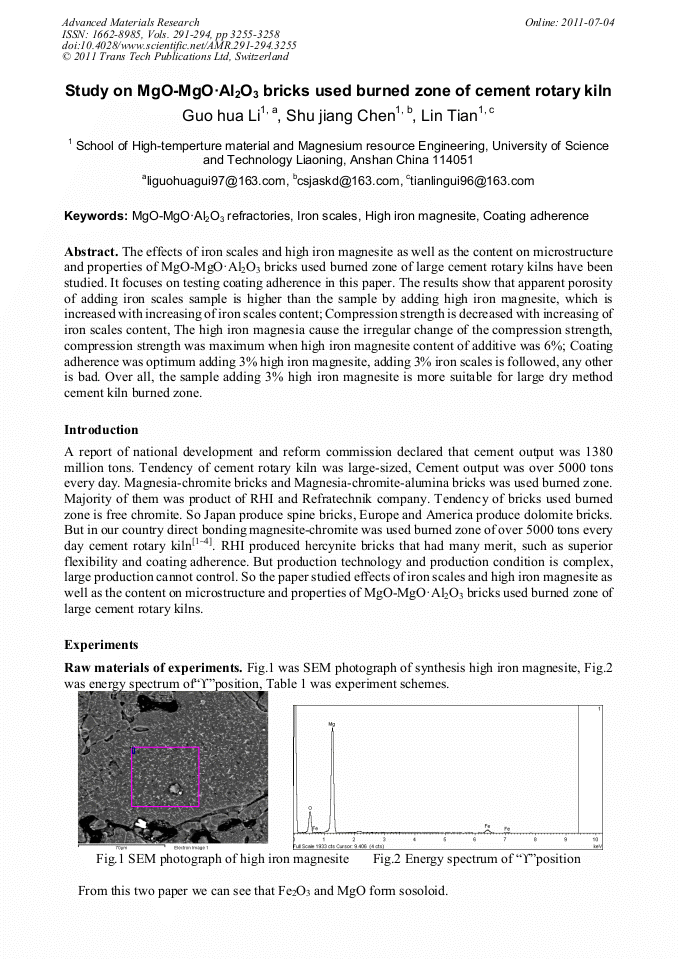
p.3255
p.3259
p.3264
p.3268
p.3272
Study on MgO-MgO•Al2O3 Bricks Used Burned Zone of Cement Rotary Kiln
Abstract:
The effects of iron scales and high iron magnesite as well as the content on microstructure and properties of MgO-MgO·Al2O3 bricks used burned zone of large cement rotary kilns have been studied. It focuses on testing coating adherence in this paper. The results show that apparent porosity of adding iron scales sample is higher than the sample by adding high iron magnesite, which is increased with increasing of iron scales content; Compression strength is decreased with increasing of iron scales content, The high iron magnesia cause the irregular change of the compression strength, compression strength was maximum when high iron magnesite content of additive was 6%; Coating adherence was optimum adding 3% high iron magnesite, adding 3% iron scales is followed, any other is bad. Over all, the sample adding 3% high iron magnesite is more suitable for large dry method cement kiln burned zone.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
3255-3258
Citation:
Online since:
July 2011
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: