p.741
p.746
p.752
p.758
p.763
p.769
p.773
p.778
p.784
Hydrodynamic Characteristics Assessment and Modeling of a Novel Membrane-Aerated Reactor
Abstract:
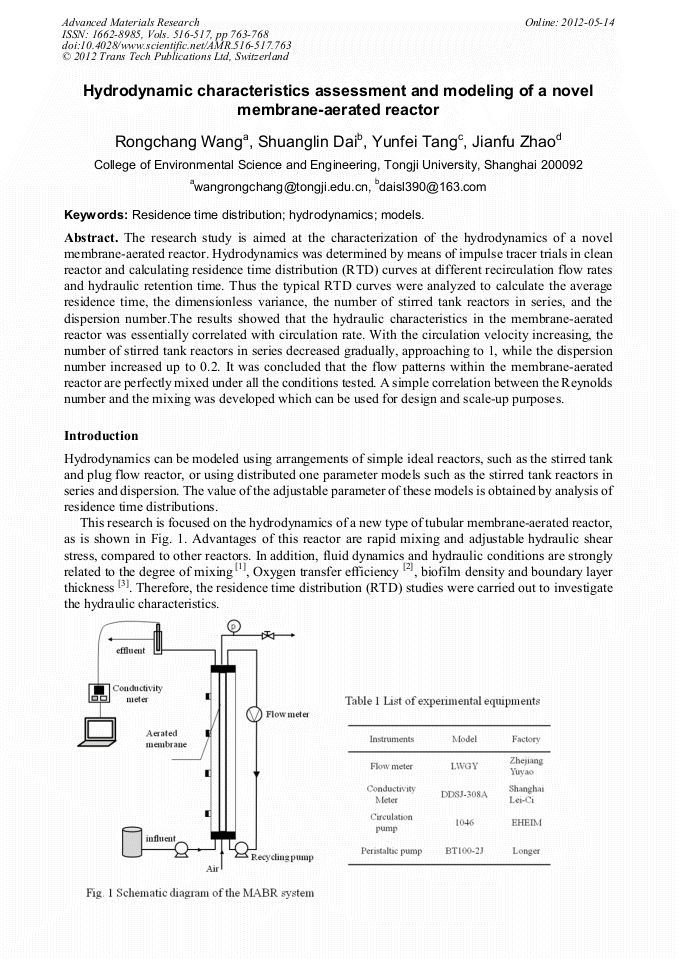
The research study is aimed at the characterization of the hydrodynamics of a novel membrane-aerated reactor. Hydrodynamics was determined by means of impulse tracer trials in clean reactor and calculating residence time distribution (RTD) curves at different recirculation flow rates and hydraulic retention time. Thus the typical RTD curves were analyzed to calculate the average residence time, the dimensionless variance, the number of stirred tank reactors in series, and the dispersion number.The results showed that the hydraulic characteristics in the membrane-aerated reactor was essentially correlated with circulation rate. With the circulation velocity increasing, the number of stirred tank reactors in series decreased gradually, approaching to 1, while the dispersion number increased up to 0.2. It was concluded that the flow patterns within the membrane-aerated reactor are perfectly mixed under all the conditions tested. A simple correlation between the Reynolds number and the mixing was developed which can be used for design and scale-up purposes.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
763-768
Citation:
Online since:
May 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: