p.2079
p.2083
p.2087
p.2092
p.2100
p.2104
p.2108
p.2112
p.2116
Thermoelectric Power Generation System with Loop Thermosyphon and TiO2-Nanofluids
Abstract:
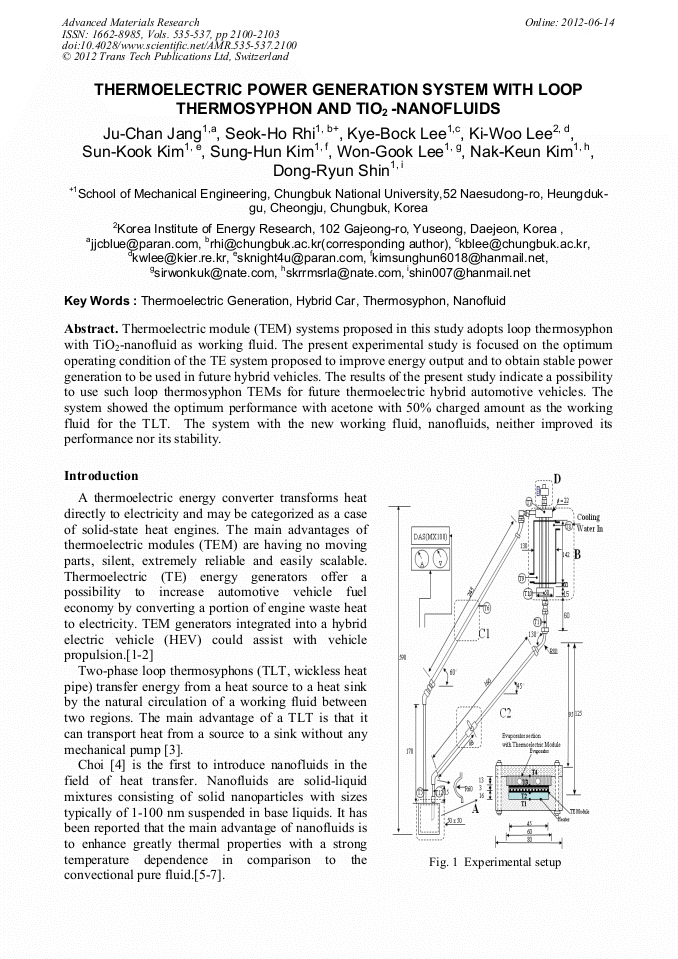
Thermoelectric module (TEM) systems proposed in this study adopts loop thermosyphon with TiO2-nanofluid as working fluid. The present experimental study is focused on the optSubscrSubscript textipt textimum operating condition of the TE system proposed to improve energy output and to obtain stable power generation to be used in future hybrid vehicles. The results of the present study indicate a possibility to use such loop thermosyphon TEMs for future thermoelectric hybrid automotive vehicles. The system showed the optimum performance with acetone with 50% charged amount as the working fluid for the TLT. The system with the new working fluid, nanofluids, neither improved its performance nor its stability.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2100-2103
Citation:
Online since:
June 2012
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: