p.2533
p.2537
p.2541
p.2546
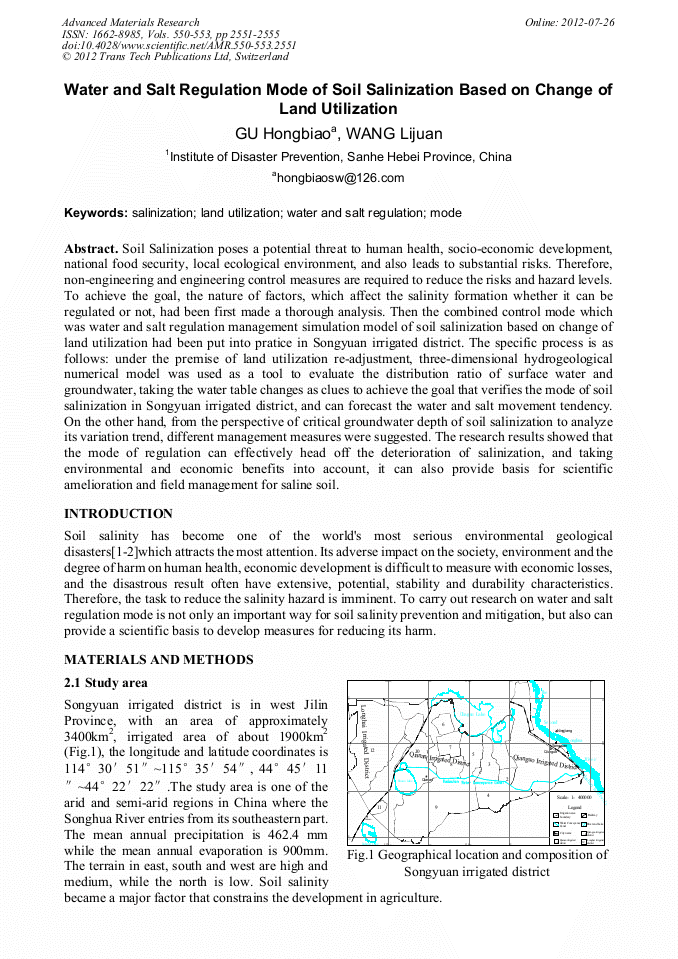
p.2551
p.2556
p.2561
p.2565
p.2571
Water and Salt Regulation Mode of Soil Salinization Based on Change of Land Utilization
Abstract:
Soil Salinization poses a potential threat to human health, socio-economic development, national food security, local ecological environment, and also leads to substantial risks. Therefore, non-engineering and engineering control measures are required to reduce the risks and hazard levels. To achieve the goal, the nature of factors, which affect the salinity formation whether it can be regulated or not, had been first made a thorough analysis. Then the combined control mode which was water and salt regulation management simulation model of soil salinization based on change of land utilization had been put into pratice in Songyuan irrigated district. The specific process is as follows: under the premise of land utilization re-adjustment, three-dimensional hydrogeological numerical model was used as a tool to evaluate the distribution ratio of surface water and groundwater, taking the water table changes as clues to achieve the goal that verifies the mode of soil salinization in Songyuan irrigated district, and can forecast the water and salt movement tendency. On the other hand, from the perspective of critical groundwater depth of soil salinization to analyze its variation trend, different management measures were suggested. The research results showed that the mode of regulation can effectively head off the deterioration of salinization, and taking environmental and economic benefits into account, it can also provide basis for scientific amelioration and field management for saline soil.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2551-2555
Citation:
Online since:
July 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: