p.1022
p.1027
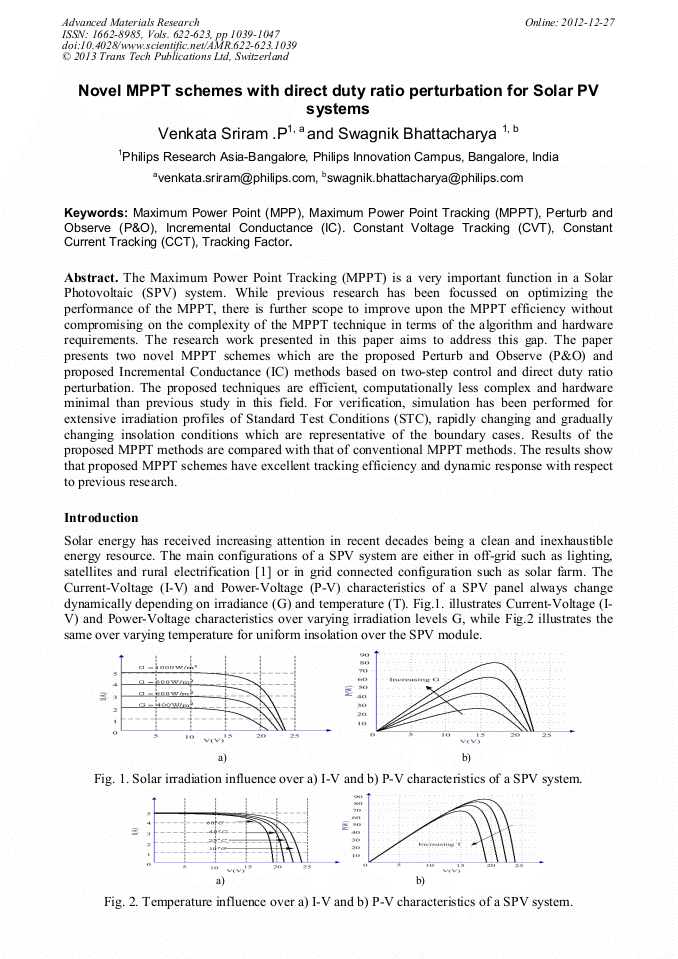
p.1030
p.1035
p.1039
p.1048
p.1056
p.1062
p.1067
Novel MPPT Schemes with Direct Duty Ratio Perturbation for Solar PV Systems
Abstract:
The Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) is a very important function in a Solar Photovoltaic (SPV) system. While previous research has been focussed on optimizing the performance of the MPPT, there is further scope to improve upon the MPPT efficiency without compromising on the complexity of the MPPT technique in terms of the algorithm and hardware requirements. The research work presented in this paper aims to address this gap. The paper presents two novel MPPT schemes which are the proposed Perturb and Observe (P&O) and proposed Incremental Conductance (IC) methods based on two-step control and direct duty ratio perturbation. The proposed techniques are efficient, computationally less complex and hardware minimal than previous study in this field. For verification, simulation has been performed for extensive irradiation profiles of Standard Test Conditions (STC), rapidly changing and gradually changing insolation conditions which are representative of the boundary cases. Results of the proposed MPPT methods are compared with that of conventional MPPT methods. The results show that proposed MPPT schemes have excellent tracking efficiency and dynamic response with respect to previous research.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1039-1047
Citation:
Online since:
December 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: