p.2774
p.2783
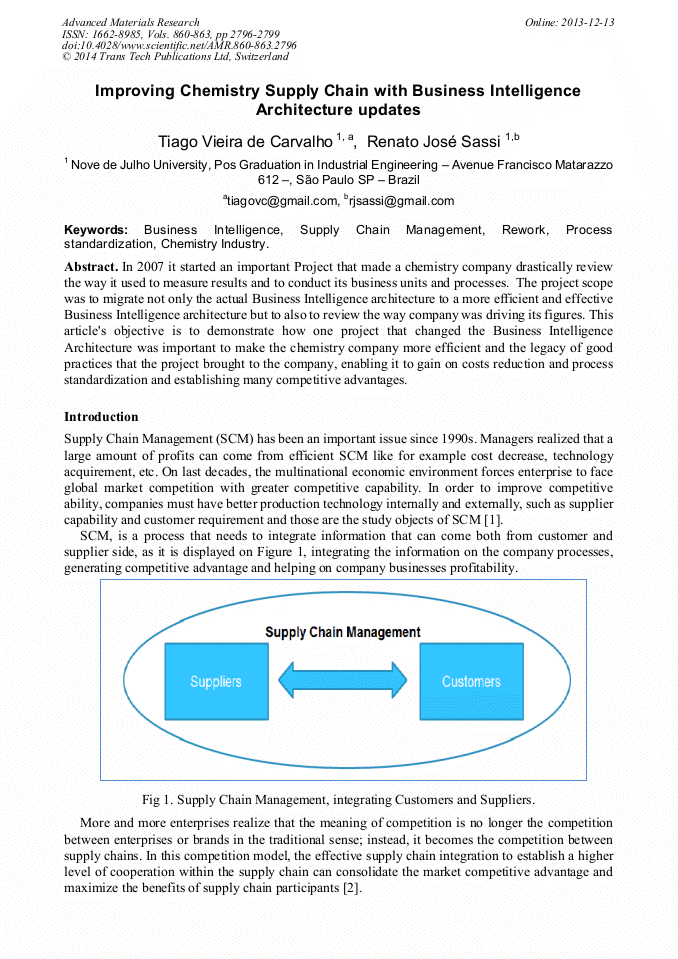
p.2787
p.2791
p.2796
p.2800
p.2804
p.2808
p.2812
Improving Chemistry Supply Chain with Business Intelligence Architecture Updates
Abstract:
In 2007 it started an important Project that made a chemistry company drastically review the way it used to measure results and to conduct its business units and processes. The project scope was to migrate not only the actual Business Intelligence architecture to a more efficient and effective Business Intelligence architecture but to also to review the way company was driving its figures. This article's objective is to demonstrate how one project that changed the Business Intelligence Architecture was important to make the chemistry company more efficient and the legacy of good practices that the project brought to the company, enabling it to gain on costs reduction and process standardization and establishing many competitive advantages.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
2796-2799
Citation:
Online since:
December 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: