p.273
p.277
p.281
p.285
p.289
p.293
p.297
p.302
p.307
Basic Principles for Integrated Building Sustainability Assessment System Focused on Carbon Emissions
Abstract:
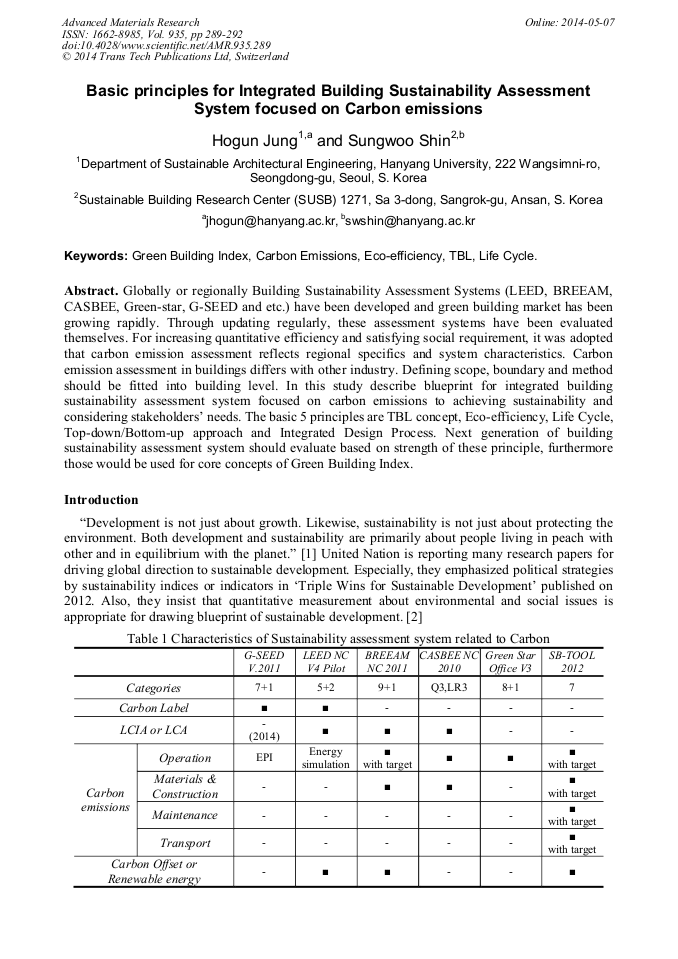
Globally or regionally Building Sustainability Assessment Systems (LEED, BREEAM, CASBEE, Green-star, G-SEED and etc.) have been developed and green building market has been growing rapidly. Through updating regularly, these assessment systems have been evaluated themselves. For increasing quantitative efficiency and satisfying social requirement, it was adopted that carbon emission assessment reflects regional specifics and system characteristics. Carbon emission assessment in buildings differs with other industry. Defining scope, boundary and method should be fitted into building level. In this study describe blueprint for integrated building sustainability assessment system focused on carbon emissions to achieving sustainability and considering stakeholders needs. The basic 5 principles are TBL concept, Eco-efficiency, Life Cycle, Top-down/Bottom-up approach and Integrated Design Process. Next generation of building sustainability assessment system should evaluate based on strength of these principle, furthermore those would be used for core concepts of Green Building Index.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
289-292
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
May 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: