p.164
p.172
p.176
p.182
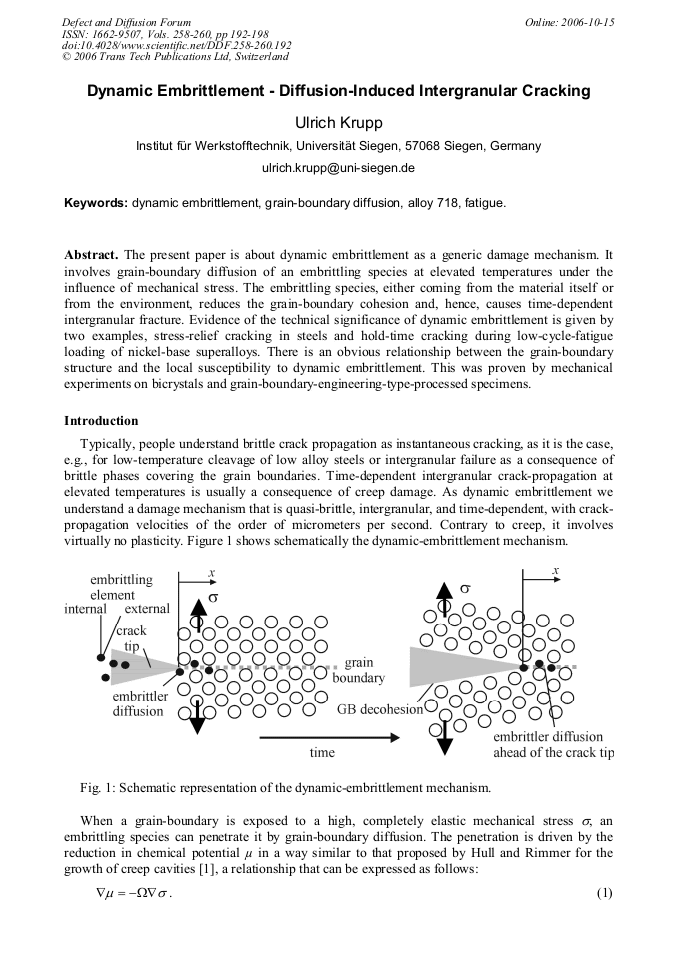
p.192
p.199
p.207
p.213
p.219
Dynamic Embrittlement - Diffusion-Induced Intergranular Cracking
Abstract:
The present paper is about dynamic embrittlement as a generic damage mechanism. It involves grain-boundary diffusion of an embrittling species at elevated temperatures under the influence of mechanical stress. The embrittling species, either coming from the material itself or from the environment, reduces the grain-boundary cohesion and, hence, causes time-dependent intergranular fracture. Evidence of the technical significance of dynamic embrittlement is given by two examples, stress-relief cracking in steels and hold-time cracking during low-cycle-fatigue loading of nickel-base superalloys. There is an obvious relationship between the grain-boundary structure and the local susceptibility to dynamic embrittlement. This was proven by mechanical experiments on bicrystals and grain-boundary-engineering-type-processed specimens.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
192-198
Citation:
Online since:
October 2006
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2006 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: