p.1046
p.1050
p.1053
p.1056
p.1060
p.1062
p.1065
p.1069
p.1072
Comparison of Spark Plasma Sintering and Hot Pressing of MgAlON
Abstract:
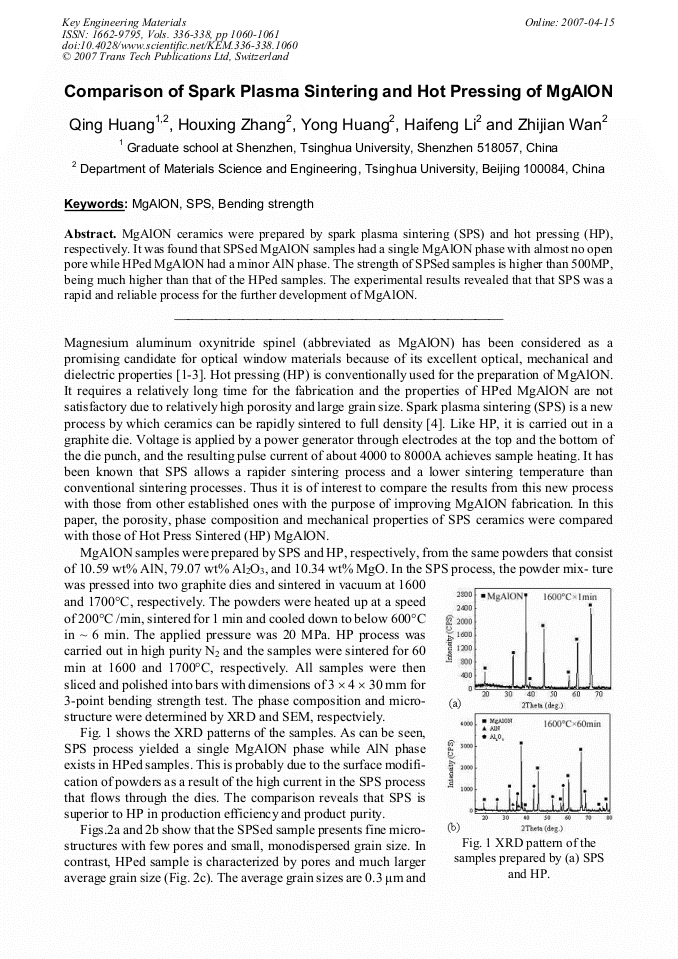
MgAlON ceramics were prepared by spark plasma sintering (SPS) and hot pressing (HP), respectively. It was found that SPSed MgAlON samples had a single MgAlON phase with almost no open pore while HPed MgAlON had a minor AlN phase. The strength of SPSed samples is higher than 500MP, being much higher than that of the HPed samples. The experimental results revealed that that SPS was a rapid and reliable process for the further development of MgAlON.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1060-1061
Citation:
Online since:
April 2007
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2007 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: