p.439
p.443
p.448
p.454
p.459
p.464
p.471
p.476
p.482
Optimum Design and Fairness of the Surfaces for Mold with Three Revolving Positions
Abstract:
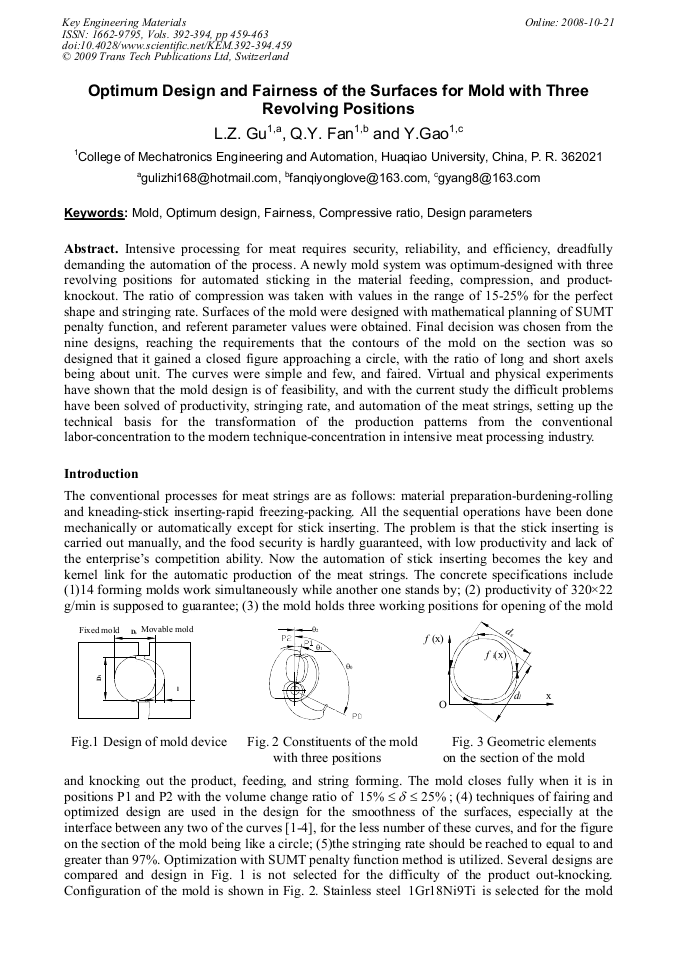
Intensive processing for meat requires security, reliability, and efficiency, dreadfully demanding the automation of the process. A newly mold system was optimum-designed with three revolving positions for automated sticking in the material feeding, compression, and productknockout. The ratio of compression was taken with values in the range of 15-25% for the perfect shape and stringing rate. Surfaces of the mold were designed with mathematical planning of SUMT penalty function, and referent parameter values were obtained. Final decision was chosen from the nine designs, reaching the requirements that the contours of the mold on the section was so designed that it gained a closed figure approaching a circle, with the ratio of long and short axels being about unit. The curves were simple and few, and faired. Virtual and physical experiments have shown that the mold design is of feasibility, and with the current study the difficult problems have been solved of productivity, stringing rate, and automation of the meat strings, setting up the technical basis for the transformation of the production patterns from the conventional labor-concentration to the modern technique-concentration in intensive meat processing industry.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
459-463
Citation:
Online since:
October 2008
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2009 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: