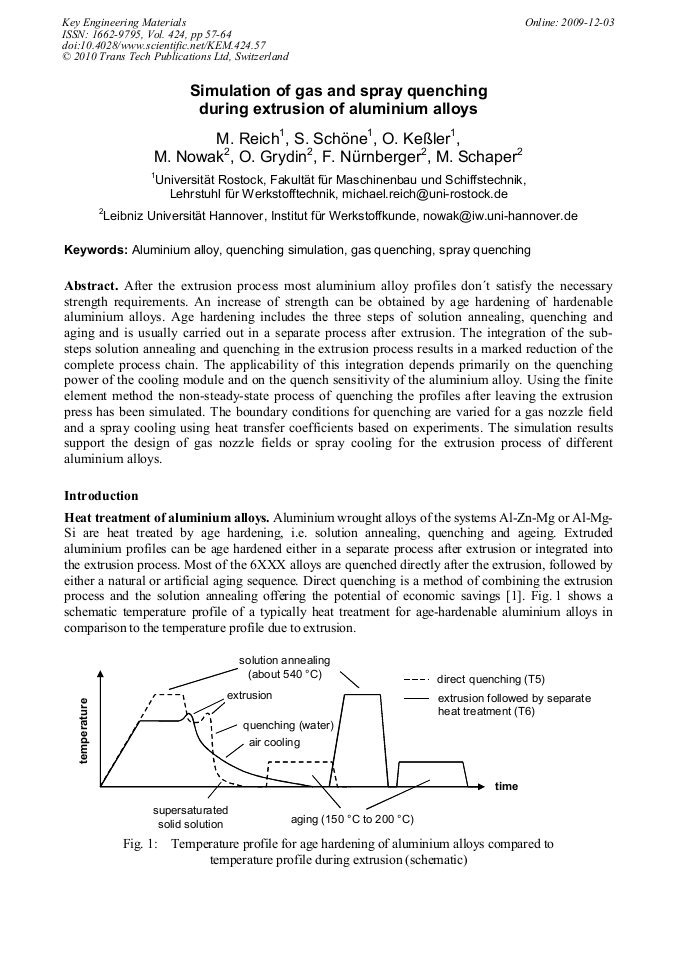
[1]
T. Sheppard: Extrusion of Aluminium Alloys, Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, (1999).
Google Scholar
[2]
D.D. Hall, I. Mudawar, R.E. Morgan, S.L. Ehlers: Validation of a Systematic Approach to Modeling Spray Quenching of Aluminum Alloy Extrusions, Composites, and Continuous Castings, in: JMEPEG vol. 6, 1997, pp.77-92.
DOI: 10.1007/s11665-997-0036-x
Google Scholar
[3]
T.A. Deiters, I. Mudawar: Optimization of Spray quenching for Aluminum Extrusion, Forging, or Continuous Casting, in: J. Heat Treat. Vol. 7, 1989, pp.9-18.
DOI: 10.1007/bf02833183
Google Scholar
[4]
C. Kramer, M. Becker: Device for Cooling Extruded Profiles, US Patent 6, 216, 485 B1, (2001).
Google Scholar
[5]
D.H. Bratland, O. Grong, H. Shercliff, O.R. Myhr, S. Tjotta: Modelling of Precipitation Reactions in Industrial Processing, in: Acta mater. Vol. 45, 1997, pp.1-22.
DOI: 10.1016/s1359-6454(96)00100-0
Google Scholar
[6]
C. Kramer: Strangabkühlung, in: J. Baumgarten: Strangpressen, DGM-Informationsges. -Verl., 1990, Oberursel, pp.119-129.
Google Scholar
[7]
N. Jaervstraet, S. Tjotta: A Process Modell for On-Line Quenching of Aluminium Alloys, in: Mateallurgical and Materials Transactions B vol. 27B, 1996, pp.501-508.
Google Scholar
[8]
C. Krause, E. Wulf, F. Nürnberger, F. -W. Bach: Wärmeübergangs- und Tropfencharakteristik für eine Spraykühlung im Temperaturbereich von 900-100 °C, in: Forsch Ingenieurwes vol. 72 (2008), pp.163-173.
DOI: 10.1007/s10010-008-0079-7
Google Scholar
[9]
C. Krause: Randschichtvergüten verzahnter Bauteile mittels einer Wasser-Luft-Spraykühlung, Dissertation, Leibniz Universität Hannover (2008).
Google Scholar
[10]
F. Puschmann: Experimentelle Untersuchung der Spraykühlung zur Qualitätsverbesserung durch definierte Einstellung des Wärmeübergangs, Dissertation, Otto-von-Guericke-Universität Magdeburg (2003).
Google Scholar
[11]
J.P. Holman: Heat Transfer, McGraw-Hill, New York, (2002).
Google Scholar
[12]
M. S Hamed: Evaluation of Heat Transfer Coefficients in Water Spray Quenching Systems, 20th Heat Treating Conf. Proc., 2000, ASM International, Vol. II, p.785.
Google Scholar
[13]
B. Milkereit, O. Kessler, C. Schick: Recording of continuous cooling precipitation diagrams of aluminium alloys, in: Thermochimica Acta, Vol. 492, Elsevier Science (2009), pp.73-78.
DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2009.01.027
Google Scholar
[14]
C. Kammer: Aluminium-Taschenbuch, edition 15, Aluminium-Verlag (1998).
Google Scholar
[15]
W. Hesse, Key to Aluminium, Aluminium-Verlag (2006).
Google Scholar
[16]
B. Milkereit, C. Schick, O. Kessler: Continuous cooling precipitation diagrams of aluminiummagnesium-silicon alloys, in: J. Hirsch, B. Skrotzki, G. Gottstein (Eds), 11th International Conference on Aluminium Alloys, Deutsche Gesellschaft für Materialkunde e.V., WILEYVCH Weinheim, Aachen, Germany, (2008).
DOI: 10.1201/9781351045636-140000288
Google Scholar
[17]
R. von Bargen, O. Kessler, H. -W. Zoch: Kontinuierliche Zeit-Ausscheidungs-Diagramme der Aluminiumlegierungen E� AW-7020 und E� AW-7050, in: HTM Z. Werkst. Wärmebeh. Fertigung 62 (2007) 6 pp.285-293.
DOI: 10.3139/105.100440
Google Scholar
[18]
M. Narazaki, M. Kogawara, M. Qin, Y. Watanabe: Measurement and Database Construction of Heat Transfer Coefficient of Gas Quenching, edited by H. -W. Zoch, Th. Lübben, Proc. 2nd Int. Conf. on Distortion Engineering, 17-19. 09. 08, Bremen, Germany, 2008, pp.327-334.
Google Scholar