p.824
p.833
p.841
p.847
p.853
p.861
p.869
p.875
p.881
Robot-Based Incremental Sheet Metal Forming – Increasing the Geometrical Accuracy of Complex Parts
Abstract:
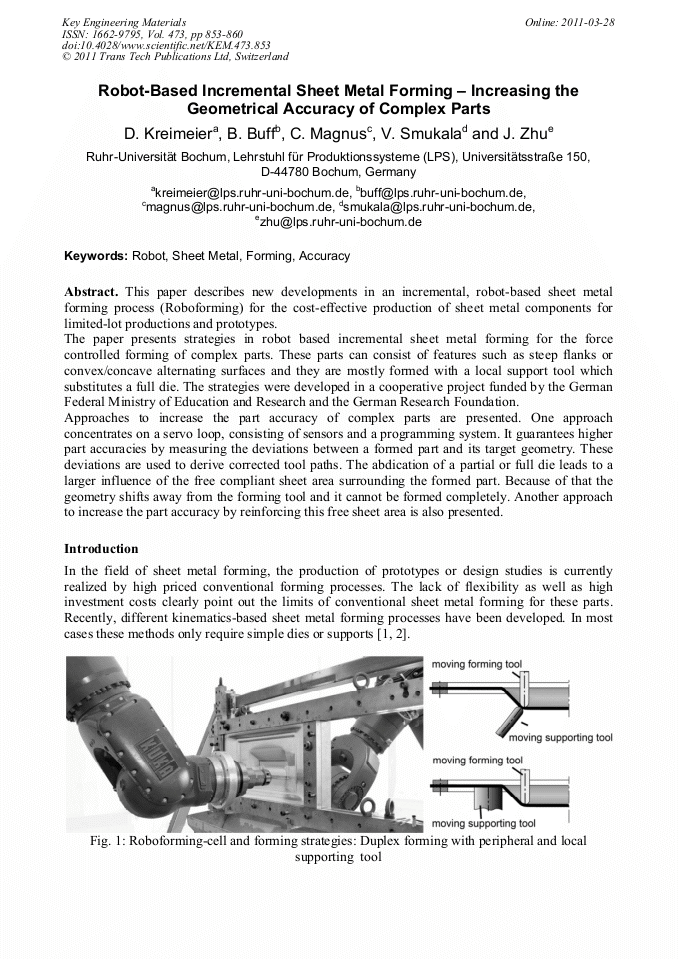
This paper describes new developments in an incremental, robot-based sheet metal forming process (Roboforming) for the cost-effective production of sheet metal components for limited-lot productions and prototypes. The paper presents strategies in robot based incremental sheet metal forming for the force controlled forming of complex parts. These parts can consist of features such as steep flanks or convex/concave alternating surfaces and they are mostly formed with a local support tool which substitutes a full die. The strategies were developed in a cooperative project funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research and the German Research Foundation. Approaches to increase the part accuracy of complex parts are presented. One approach concentrates on a servo loop, consisting of sensors and a programming system. It guarantees higher part accuracies by measuring the deviations between a formed part and its target geometry. These deviations are used to derive corrected tool paths. The abdication of a partial or full die leads to a larger influence of the free compliant sheet area surrounding the formed part. Because of that the geometry shifts away from the forming tool and it cannot be formed completely. Another approach to increase the part accuracy by reinforcing this free sheet area is also presented.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
853-860
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
March 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: