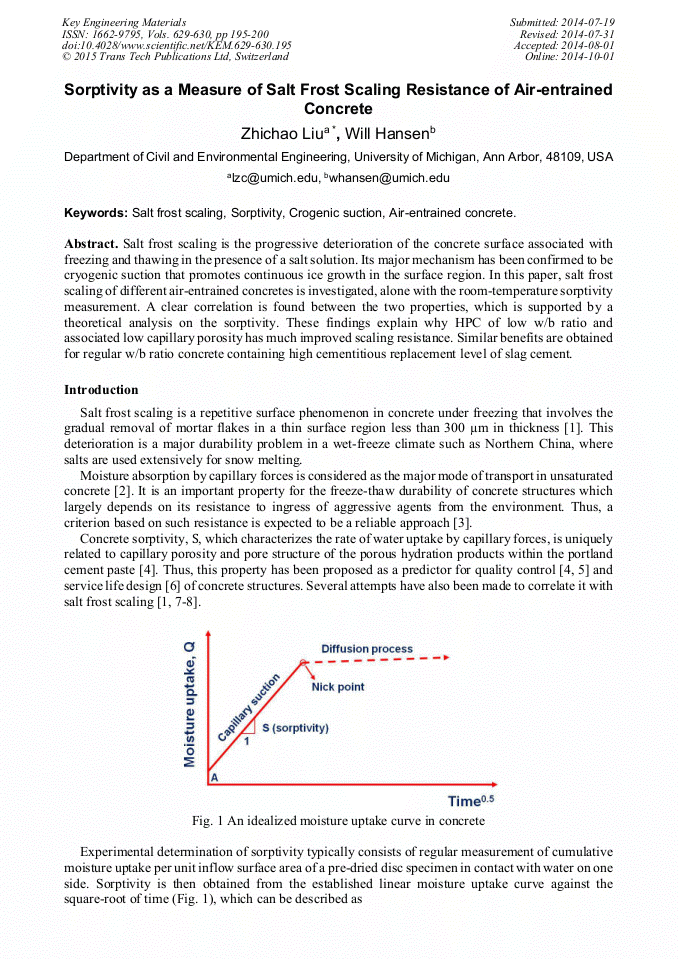
[1]
Z. Liu, W. Hansen, Cryogenic suction as a major salt frost scaling mechanism in cementitious materials: Submitted to Journal of Cement and Concrete Research (2014).
Google Scholar
[2]
N. Martys, C. E Ferraris, Capillary transport in mortars and concrete, Cem. Concr. Res. 27 (1997) 747-760.
DOI: 10.1016/s0008-8846(97)00052-5
Google Scholar
[3]
J. Kropp, Relations between transport characteristics and durability, in: J. Kropp, H.K. Hilsdorf (Eds. ), Performance Criteria for Concrete Durability, Chapman & Hall, London, 1995, pp.97-137.
DOI: 10.1201/9781482271522
Google Scholar
[4]
Note from E.J. Sellevold (Liquid permeability, capillary suction: PF-method), (1990).
Google Scholar
[5]
V.L. Taus, A.A. Di Maio, L.P. Traversa, Sorptivity: parameter for the evaluation of cover concrete quality, ACI SP (229) 2005 121-134.
Google Scholar
[6]
D.P. Bentz, M.A. Ehlen, C.F. Ferraris, E.J. Garboczi, Sorptivity-based service life predictions for concrete pavements, Proceedings of 7th International Conference on Concrete Pavements, Volume1, International Society for Concrete Pavements, Orlando, Florida, 2001, pp.181-193.
DOI: 10.3403/30028566u
Google Scholar
[7]
R. Gagné, E. Houehanou, M. Jolin, P. Escaffit, Study of the relationship between scaling resistance and sorptivity of concrete, Can. J. Civil Eng. 38 (11) (2011) 1238-1248.
DOI: 10.1139/l11-084
Google Scholar
[8]
S.E. Chidiac, D.K. Panesar, Sorptivity of concrete as an indicator of laboratory freeze-thaw scaling performance, in: V. Baroghel-Bouny, C. Andrade, R. Torrent, K. Scrivener (Eds. ), International RILEM Workshop on Performance Based Evaluation and Indicators for Concrete Durability, Madrid, Spain, 2006, pp.59-66.
DOI: 10.1617/291214390x.028
Google Scholar
[9]
C. Hall, Water movement in porous building materials-I. unsaturated flow theory and its application, Bldgn. Envir. 12 (1977) 117-125.
DOI: 10.1016/0360-1323(77)90040-3
Google Scholar
[10]
M.J. Setzer, Test methods of frost resistance of concrete: CIF-Test: Capillary suction, Internal damage and Freeze thaw Test-Reference method and alternative methods A and B, Mater. Struct. 37 (2004) 743-753.
DOI: 10.1617/14143
Google Scholar
[11]
S. Lindmark, Mechanisms of salt frost scaling of Portland cement-bound materials: Studies and hypothesis, PhD thesis, Lund Institute of Technology, (1998).
Google Scholar
[12]
J. Kaufmann, Experimental identification of damage mechanisms in cementitious porous materials on phase transition of pore solution under frost deicing salt attack, PhD Dissertation, Swiss Federal Institute of Technology Lausanne (EPFL), (2000).
Google Scholar
[13]
E.W. Washburn, The dynamics of capillary flow, Phys. Rev. 17 (3) (1921) 273-283.
Google Scholar