p.140
p.144
p.149
p.155
p.162
p.167
p.172
p.178
p.183
The Assessment of Cutting Temperature Measurements in High-Speed Machining
Abstract:
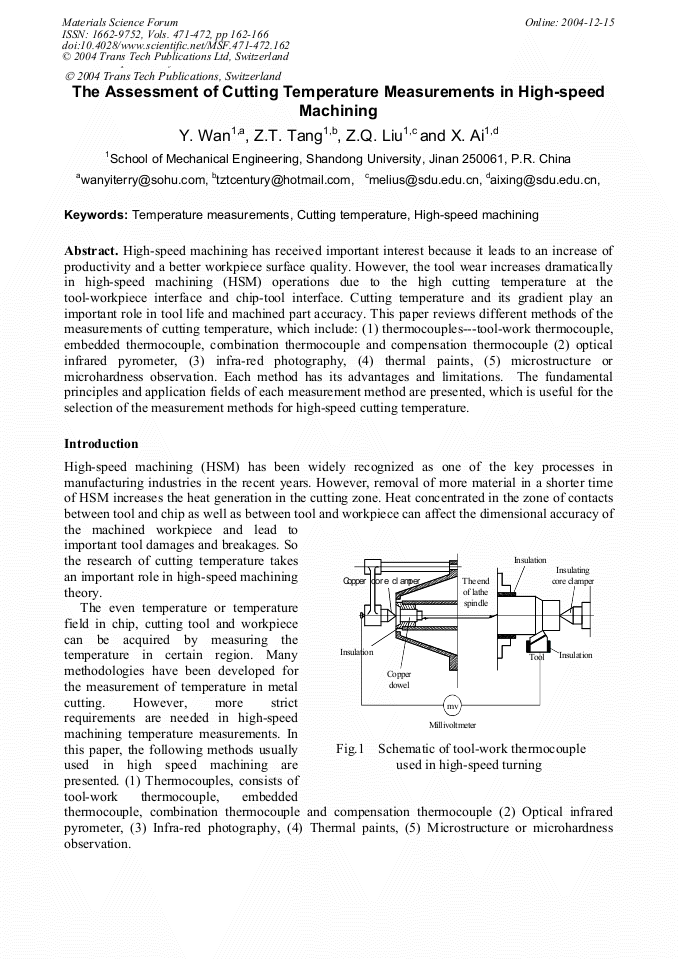
High-speed machining has received important interest because it leads to an increase of productivity and a better workpiece surface quality. However, the tool wear increases dramatically in high-speed machining (HSM) operations due to the high cutting temperature at the tool-workpiece interface and chip-tool interface. Cutting temperature and its gradient play an important role in tool life and machined part accuracy. This paper reviews different methods of the measurements of cutting temperature, which include: (1) thermocouples---tool-work thermocouple, embedded thermocouple, combination thermocouple and compensation thermocouple (2) optical infrared pyrometer, (3) infra-red photography, (4) thermal paints, (5) microstructure or microhardness observation. Each method has its advantages and limitations. The fundamental principles and application fields of each measurement method are presented, which is useful for the selection of the measurement methods for high-speed cutting temperature.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
162-166
Citation:
Online since:
December 2004
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2004 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: