p.313
p.319
p.325
p.331
p.337
p.343
p.349
p.354
p.360
Machining Profiling of the Working Rolls as a Way to Control Cross-Section of the Rolled Steel
Abstract:
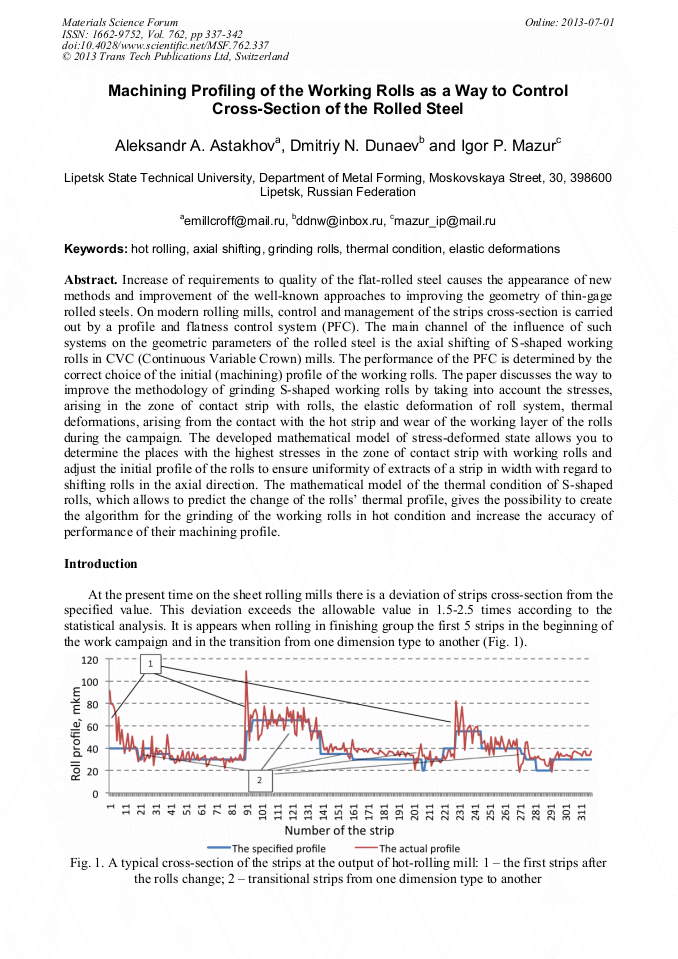
ncrease of requirements to quality of the flat-rolled steel causes the appearance of new methods and improvement of the well-known approaches to improving the geometry of thin-gage rolled steels. On modern rolling mills, control and management of the strips cross-section is carried out by a profile and flatness control system (PFC). The main channel of the influence of such systems on the geometric parameters of the rolled steel is the axial shifting of S-shaped working rolls in CVC (Continuous Variable Crown) mills. The performance of the PFC is determined by the correct choice of the initial (machining) profile of the working rolls. The paper discusses the way to improve the methodology of grinding S-shaped working rolls by taking into account the stresses, arising in the zone of contact strip with rolls, the elastic deformation of roll system, thermal deformations, arising from the contact with the hot strip and wear of the working layer of the rolls during the campaign. The developed mathematical model of stress-deformed state allows you to determine the places with the highest stresses in the zone of contact strip with working rolls and adjust the initial profile of the rolls to ensure uniformity of extracts of a strip in width with regard to shifting rolls in the axial direction. The mathematical model of the thermal condition of S-shaped rolls, which allows to predict the change of the rolls thermal profile, gives the possibility to create the algorithm for the grinding of the working rolls in hot condition and increase the accuracy of performance of their machining profile.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
337-342
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
July 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: