p.28
p.33
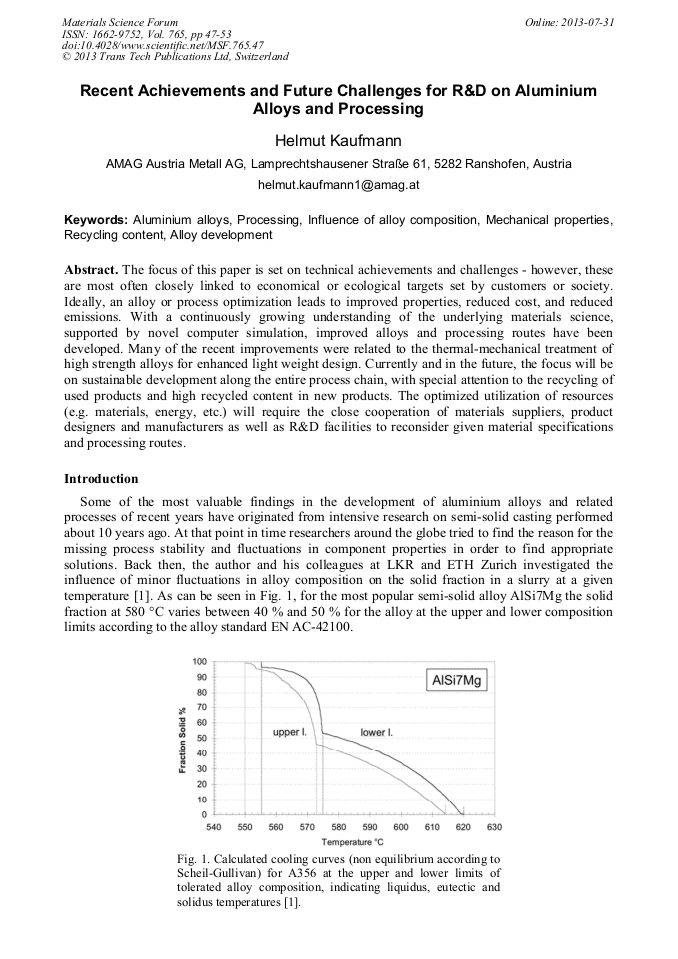
p.38
p.42
p.47
p.54
p.59
p.64
p.69
Recent Achievements and Future Challenges for R&D on Aluminium Alloys and Processing
Abstract:
The focus of this paper is set on technical achievements and challenges - however, these are most often closely linked to economical or ecological targets set by customers or society. Ideally, an alloy or process optimization leads to improved properties, reduced cost, and reduced emissions. With a continuously growing understanding of the underlying materials science, supported by novel computer simulation, improved alloys and processing routes have been developed. Many of the recent improvements were related to the thermal-mechanical treatment of high strength alloys for enhanced light weight design. Currently and in the future, the focus will be on sustainable development along the entire process chain, with special attention to the recycling of used products and high recycled content in new products. The optimized utilization of resources (e.g. materials, energy, etc.) will require the close cooperation of materials suppliers, product designers and manufacturers as well as R&D facilities to reconsider given material specifications and processing routes.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
47-53
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
July 2013
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: