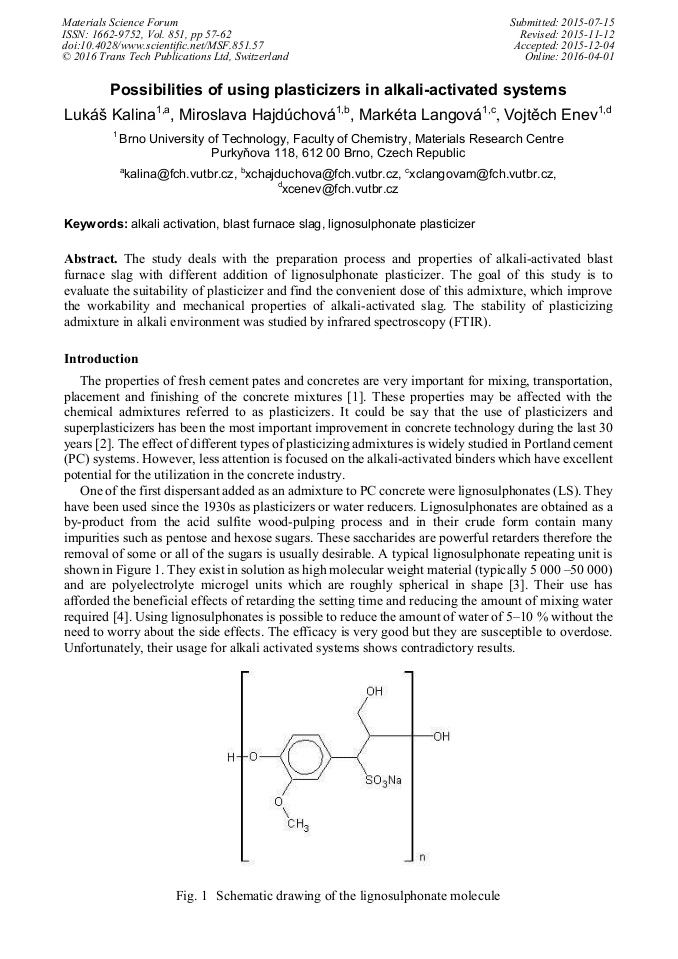
[1]
C. Shi, P.V. Krivenko, D. Roy, Alkali-activated cements and concretes, Taylor & Francis, London, 2006, ISBN 04-157-0004-3.
DOI: 10.4324/9780203390672
Google Scholar
[2]
M. Collepardi, The new concrete, Grafiche Tintoretto, Villorba, 2006, ISBN 88-903777-2-0.
Google Scholar
[3]
P.C. Hewlett, Lea´s Chemistry of cement and concrete, Butterworth-Heinemann, Oxford, 2004, ISBN-978-0-7506-6256-7.
Google Scholar
[4]
N. Roussel, Understanding the rheology of concrete. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge, 2012, ISBN 978-0-85709-028-7.
Google Scholar
[5]
E. Douglas, J. Brandštetr, A preliminary study on the alkali activation of ground granulated blast furnace slag, Cem. Concr. Res. 20 (1990), 746-756.
DOI: 10.1016/0008-8846(90)90008-l
Google Scholar
[6]
K. Isozaki, S. Iwamoto, K. Nakagawa, Some properties of alkali-activated slag cements, CAJ Review (1986), 120-123.
Google Scholar
[7]
T. Bakharev, J.G. Sanjayan, Y.B. Cheng, Effect of admixtures on the properties of alkali-activated slag concrete, Cem. Concr. Res. 30 (2000), 1367-1374.
DOI: 10.1016/s0008-8846(00)00349-5
Google Scholar
[8]
S.D. Wang, K.L. Scrivener, P.L. Pratt, Factors affecting the strength of alkali-activated slag, Cem. Concr. Res. 24 (1994), 1033-1043.
DOI: 10.1016/0008-8846(94)90026-4
Google Scholar
[9]
H.H. Darweesh, Effect of the combination of some pozzolanic wastes on the properties of Portland cement pastes, IIC 808 (2005), 298-311.
Google Scholar
[10]
A. Kashani, J.L. Provis, J. Xu, A.R. Kilcullen, G.G. Qiao, J.S.J. van Deventer, Effect of molecular architecture of polycarboxylate ethers on plasticizing performance in alkali-activated slag paste, J. Mater. Sci. 49 (2014), 2761-2772.
DOI: 10.1007/s10853-013-7979-0
Google Scholar