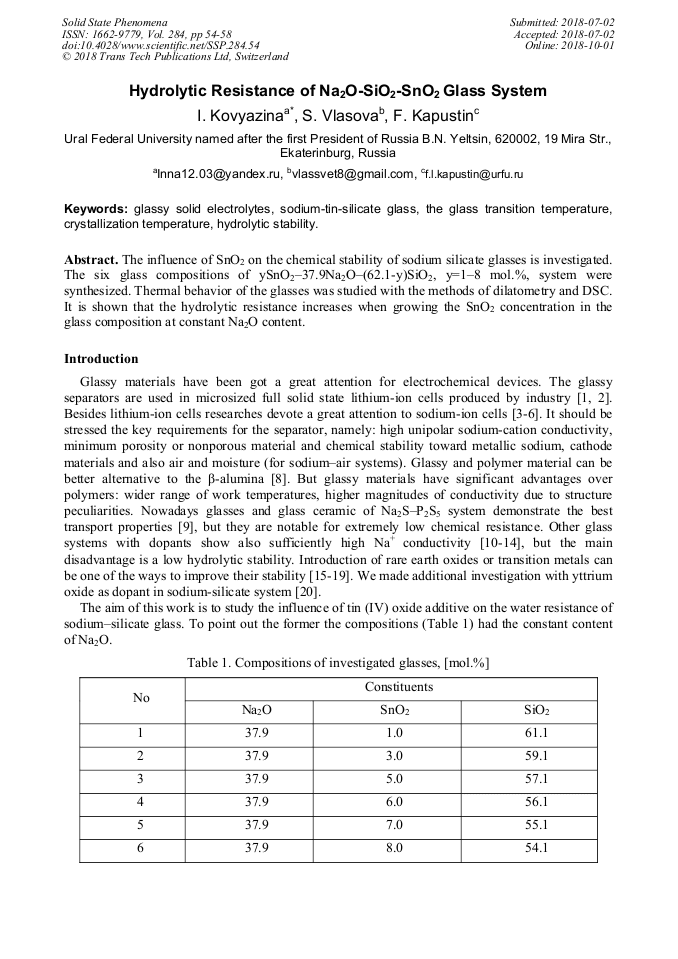
[1]
J.L. Souquet, M. Duclot, Thin film lithium batteries, J. Solid State Ionics. 148 (2002) 375-379.
DOI: 10.1016/s0167-2738(02)00076-0
Google Scholar
[2]
X.H. Yu, A stable thin-film lithium electrolyte: Lithium phosphorus oxynitride, J. Electrochem. Soc. 144 (1997) 2, 524-532.
DOI: 10.1149/1.1837443
Google Scholar
[3]
B.L. Ellis, L.F. Nazar, Sodium and sodium-ion energy storage batteries, J. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science. 16 (2012) 168-177.
DOI: 10.1016/j.cossms.2012.04.002
Google Scholar
[4]
P. Adelhelm, P. Hartmann, From lithium to sodium: cell chemistry of room temperature sodium–air and sodium–sulfur batteries, Beilstein J. Nanotechnol. 6 (2015) 1016-1055.
DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.6.105
Google Scholar
[5]
N. Yabuuchi, K. Kubota, M. Dahbi, S. Komaba, Research development on sodium-ion batteries, J. Chem. Rev. 114 (2014) 23, 11636-11682.
DOI: 10.1021/cr500192f
Google Scholar
[6]
H. Kim, J.-S. Park, S.-H. Sahgong, S. Park, J.-K. Kim, Metal-free hybrid seawater fuel cell with an etherbased electrolyte, J. Mater. Chem. 2 (2014) 19584-19588.
DOI: 10.1039/c4ta04937c
Google Scholar
[7]
T. Oshima, M. Kajita, Development of sodium – sulfur batteries, Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol. 1 (2004) 269.
Google Scholar
[8]
T. Minami, M. Tatsumisago, M. Wakihara, C. Iwakura, S. Kohjiya, I. Tanaka, Solid State Ionics for Batteries. (2005).
DOI: 10.1007/4-431-27714-5
Google Scholar
[9]
A. Hayashi et al, J. Nat. Commun. 3 (2012) 856.
Google Scholar
[10]
C.C. Hunter, M.D. Ingram, Na+-Ion conducting glasses, J. Solid State Ionics. 14 (1984) 1, 31.
DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(84)90007-9
Google Scholar
[11]
M.D. Ingram, Amorphous Materials: Ionic Transport in: K. H. Jürgen Buschow, Robert W. Cahn, Merton C. Flemings and Edward J. Kramer (eds), Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, Elsevier Ltd, the USA, 2001, 204-211.
DOI: 10.1016/b0-08-043152-6/00044-9
Google Scholar
[12]
M.D. Ingram, Amorphous Materials: Mixed Alkali Effect in: K. H. Jürgen Buschow, Robert W. Cahn, Merton C. Flemings and Edward J. Kramer (eds), Encyclopedia of Materials: Science and Technology, Elsevier Ltd, the USA, 2001, 220-223.
DOI: 10.1016/b0-08-043152-6/00047-4
Google Scholar
[13]
A. Paraskiva, M. Bokova, E. Bychkov, Na+ ion conducting glasses in the NaCl-Ga2S3-GeS2 system: A critical percolation regime, J. Solid State Ion. 299 (2017) 2-7.
DOI: 10.1016/j.ssi.2016.11.003
Google Scholar
[14]
C. Ragoen, S. Sen, T. Lambricht, S. Godet, Effect of Al2O3 content on the mechanical and interdiffusional properties of ion-exchanged Na-aluminosilicate glasses, J. of Non-Cryst. Solids. 458 (2017) 129-136.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.12.019
Google Scholar
[15]
M.G. Alexander, B. Riley, Ion-conducting glasses in the Na2O–Y2O3–SiO2 and Li2O–Y2O3–SiO2 systems, J. Solid State Ion. 18, 19 (1986) 478-482.
DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(86)90163-3
Google Scholar
[16]
M.G. Alexander, Effect of modifier cations on Na+ conductivity in sodium silicate glasses, J. Solid State Ion. 22 (1987) 257-260.
DOI: 10.1016/0167-2738(87)90042-7
Google Scholar
[17]
Bhupinder Kaur, K. Singh, O.P. Pandey, Samita Thakur, Influence of modifier on dielectric and ferroelectric properties of aluminosilicate glasses, J. of Non-Cryst. Solids. 465 (2017) 26-30.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.03.032
Google Scholar
[18]
Fuji Funabiki, Tetsuji Yano, Shuichi Shibata, Masayuki Yamane, Electrical conductivity of Ag+/Na+ ion-exchanged titanosilicate glasses, J. Solid State Ion. 160 (2003) 281-288.
DOI: 10.1016/s0167-2738(03)00168-1
Google Scholar
[19]
C. Calahooa, J.W. Zwanziger, The mixed modifier effect in ionic conductivity and mechanical properties for xMgO-(50-x)CaO-50SiO2 glasses, J. of Non-Cryst. Solids. 460 (2017) 6-18.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2017.01.017
Google Scholar
[20]
G.V. Nechaev, S.G. Vlasova, I.S. Kovyazina, O.G. Reznitskich, Transport properties of the sodium-yttrium-silicate glasses, J. of Non-Cryst. Solids. 445-446 (2016) 30-33.
DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.04.044
Google Scholar
[21]
I.S. Kovyazina, S.G. Vlasova, G.V. Nechaev, O.G. Reznitskich, Physical–chemical properties and conductivity of Na2O–SnO2–SiO2 glass systems, J. Glass physics and chemistry. 43 (2017) 2, 146-150.
DOI: 10.1134/s1087659617020080
Google Scholar