p.1175
p.1181
p.1187
p.1197
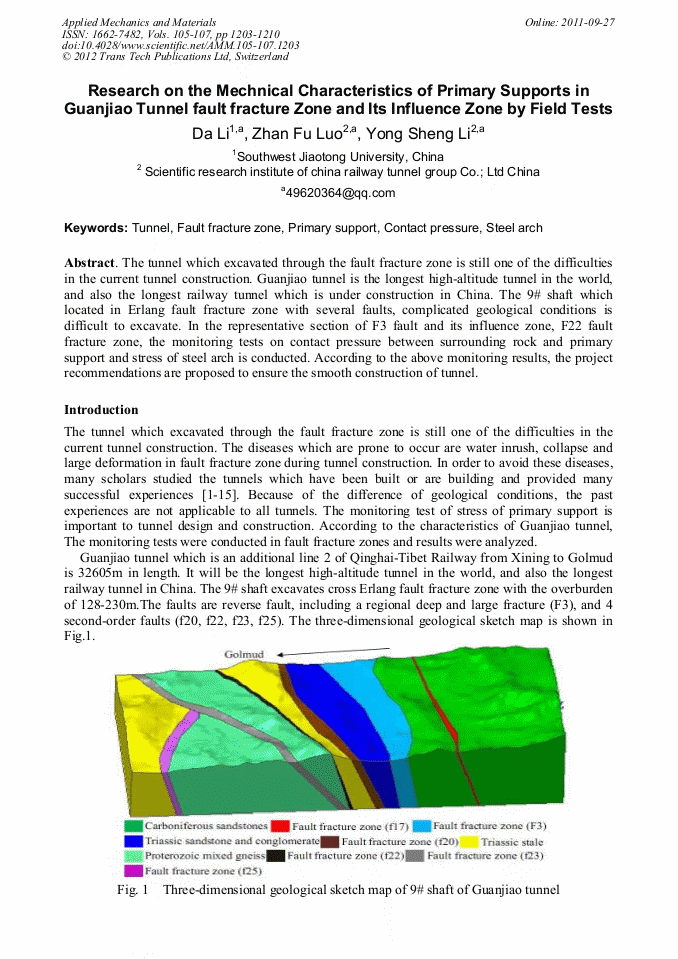
p.1203
p.1211
p.1215
p.1220
p.1225
Research on the Mechnical Characteristics of Primary Supports in Guanjiao Tunnel Fault Fracture Zone and its Influence Zone by Field Tests
Abstract:
The tunnel which excavated through the fault fracture zone is still one of the difficulties in the current tunnel construction. Guanjiao tunnel is the longest high-altitude tunnel in the world, and also the longest railway tunnel which is under construction in China. The 9# shaft which located in Erlang fault fracture zone with several faults, complicated geological conditions is difficult to excavate. In the representative section of F3 fault and its influence zone, F22 fault fracture zone, the monitoring tests on contact pressure between surrounding rock and primary support and stress of steel arch is conducted. According to the above monitoring results,the project recommendations are proposed to ensure the smooth construction of tunnel.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1203-1210
Citation:
Online since:
September 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: