p.3982
p.3986
p.3994
p.3998
p.4002
p.4006
p.4011
p.4016
p.4020
Performance Analysis of CAES Power Plant Energy Storage Sub-System for Wind Power
Abstract:
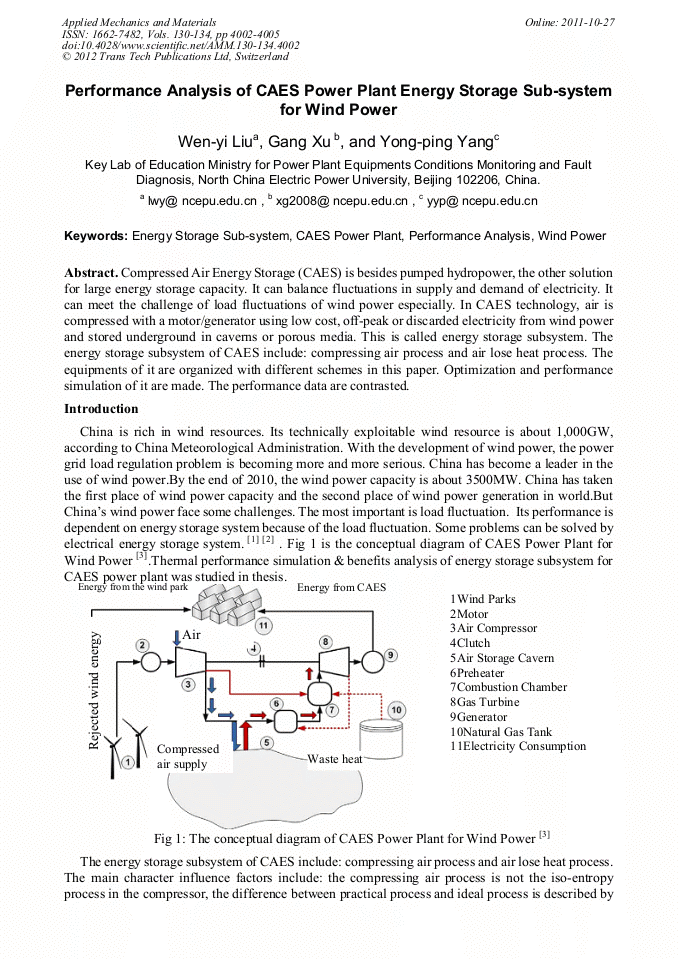
Compressed Air Energy Storage (CAES) is besides pumped hydropower, the other solution for large energy storage capacity. It can balance fluctuations in supply and demand of electricity. It can meet the challenge of load fluctuations of wind power especially. In CAES technology, air is compressed with a motor/generator using low cost, off-peak or discarded electricity from wind power and stored underground in caverns or porous media. This is called energy storage subsystem. The energy storage subsystem of CAES include: compressing air process and air lose heat process. The equipments of it are organized with different schemes in this paper. Optimization and performance simulation of it are made. The performance data are contrasted.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
4002-4005
Citation:
Online since:
October 2011
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: