p.954
p.960
p.964
p.970
p.976
p.982
p.987
p.991
p.996
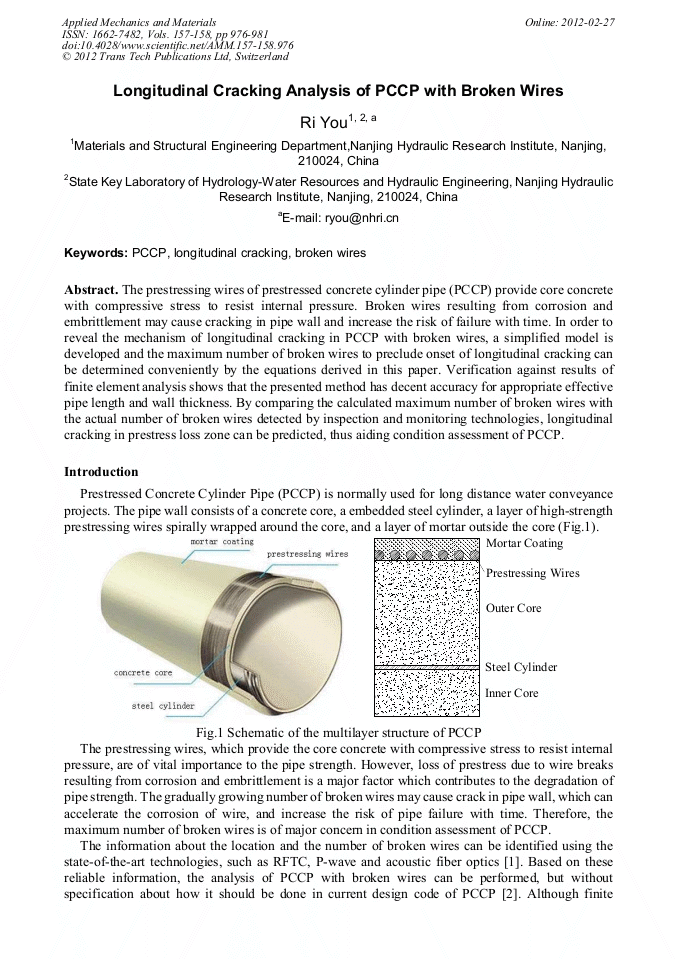
Longitudinal Cracking Analysis of PCCP with Broken Wires
Abstract:
The prestressing wires of prestressed concrete cylinder pipe (PCCP) provide core concrete with compressive stress to resist internal pressure. Broken wires resulting from corrosion and embrittlement may cause cracking in pipe wall and increase the risk of failure with time. In order to reveal the mechanism of longitudinal cracking in PCCP with broken wires, a simplified model is developed and the maximum number of broken wires to preclude onset of longitudinal cracking can be determined conveniently by the equations derived in this paper. Verification against results of finite element analysis shows that the presented method has decent accuracy for appropriate effective pipe length and wall thickness. By comparing the calculated maximum number of broken wires with the actual number of broken wires detected by inspection and monitoring technologies, longitudinal cracking in prestress loss zone can be predicted, thus aiding condition assessment of PCCP.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
976-981
Citation:
Online since:
February 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: