p.1201
p.1206
p.1211
p.1218
p.1224
p.1229
p.1234
p.1239
p.1244
Vibration Character Analysis and Calculation for Hemispherical Resonator Gyro
Abstract:
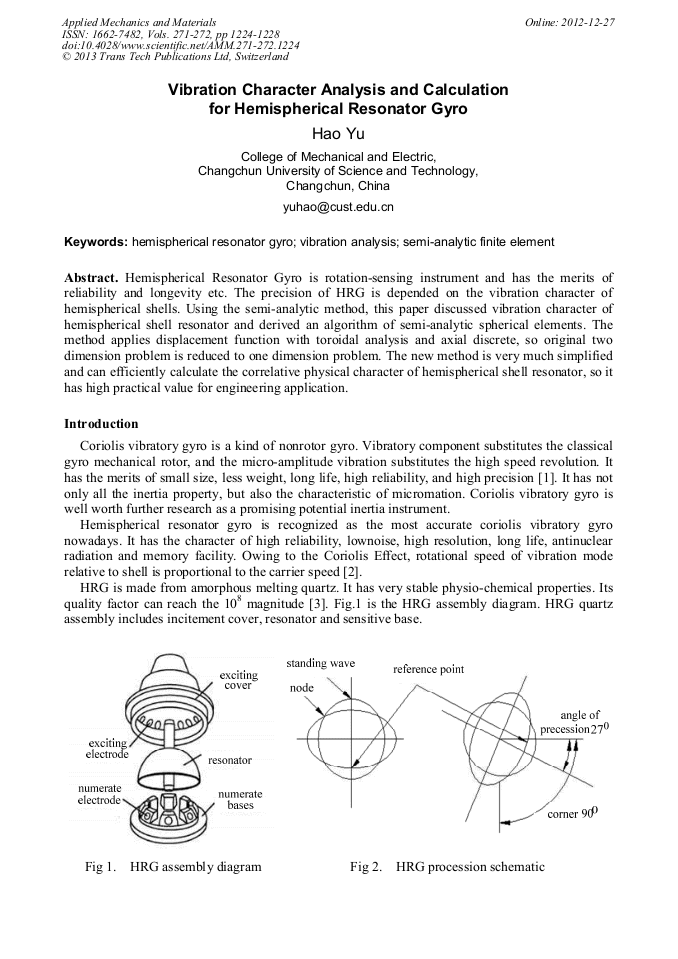
Hemispherical Resonator Gyro is rotation-sensing instrument and has the merits of reliability and longevity etc. The precision of HRG is depended on the vibration character of hemispherical shells. Using the semi-analytic method, this paper discussed vibration character of hemispherical shell resonator and derived an algorithm of semi-analytic spherical elements. The method applies displacement function with toroidal analysis and axial discrete, so original two dimension problem is reduced to one dimension problem. The new method is very much simplified and can efficiently calculate the correlative physical character of hemispherical shell resonator, so it has high practical value for engineering application.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1224-1228
Citation:
Online since:
December 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2013 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: