p.298
p.304
p.311
p.315
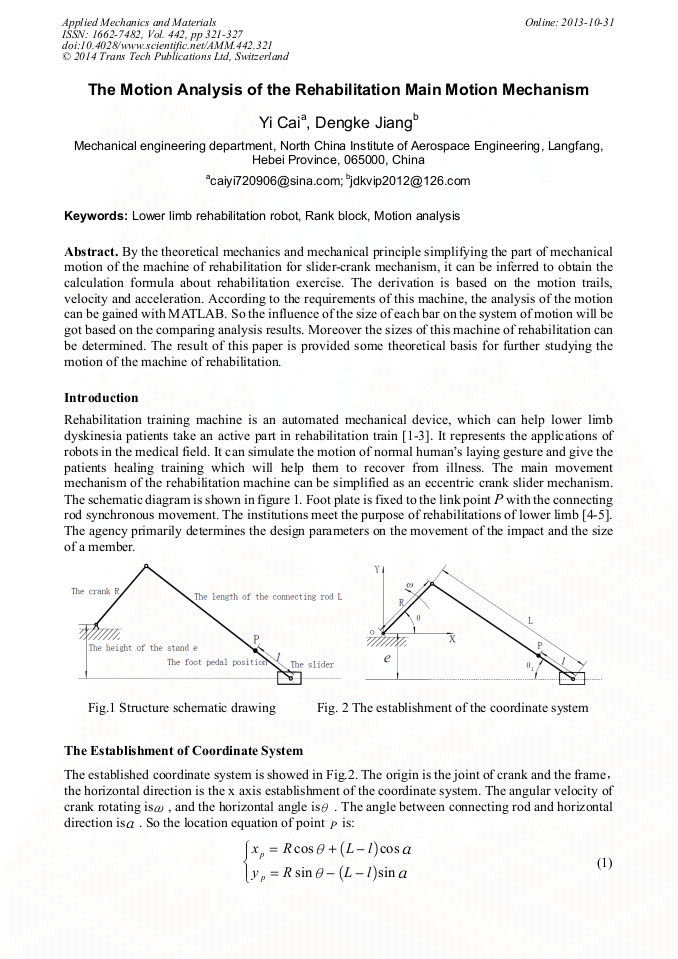
p.321
p.328
p.332
p.338
p.342
The Motion Analysis of the Rehabilitation Main Motion Mechanism
Abstract:
By the theoretical mechanics and mechanical principle simplifying the part of mechanical motion of the machine of rehabilitation for slider-crank mechanism, it can be inferred to obtain the calculation formula about rehabilitation exercise. The derivation is based on the motion trails, velocity and acceleration. According to the requirements of this machine, the analysis of the motion can be gained with MATLAB. So the influence of the size of each bar on the system of motion will be got based on the comparing analysis results. Moreover the sizes of this machine of rehabilitation can be determined. The result of this paper is provided some theoretical basis for further studying the motion of the machine of rehabilitation.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
321-327
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
October 2013
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: