p.3945
p.3949
p.3952
p.3956
p.3961
p.3965
p.3972
p.3976
p.3980
A Model of the Geometric Tolerances Modeling and Representation Process
Abstract:
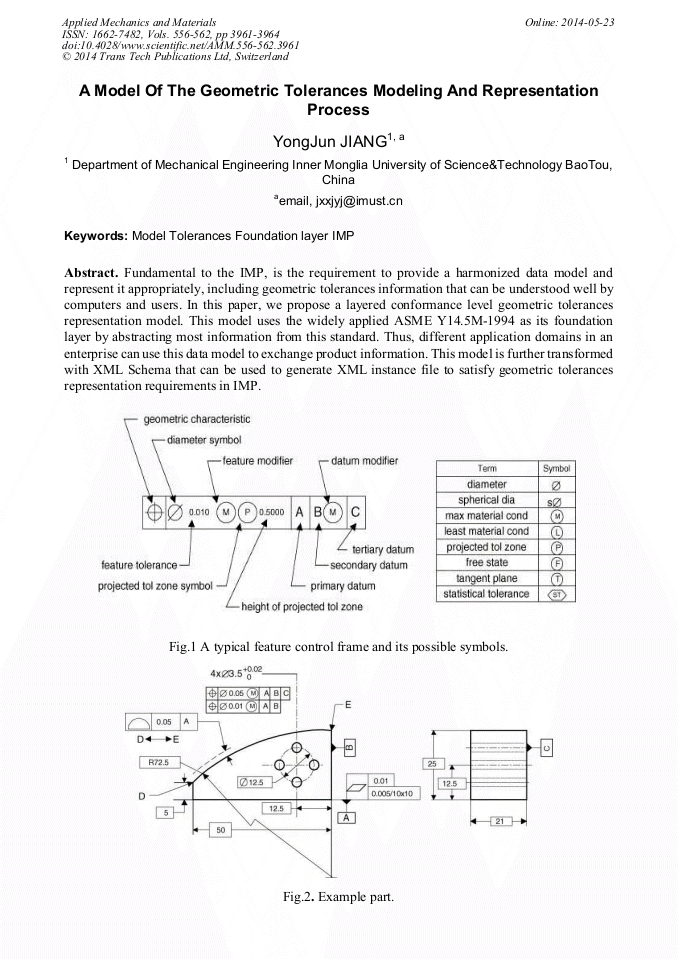
Fundamental to the IMP, is the requirement to provide a harmonized data model and represent it appropriately, including geometric tolerances information that can be understood well by computers and users. In this paper, we propose a layered conformance level geometric tolerances representation model. This model uses the widely applied ASME Y14.5M-1994 as its foundation layer by abstracting most information from this standard. Thus, different application domains in an enterprise can use this data model to exchange product information. This model is further transformed with XML Schema that can be used to generate XML instance file to satisfy geometric tolerances representation requirements in IMP. Fig.1 A typical feature control frame and its possible symbols. Fig.2. Example part.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
3961-3964
Citation:
Online since:
May 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: