p.1137
p.1141
p.1146
p.1151
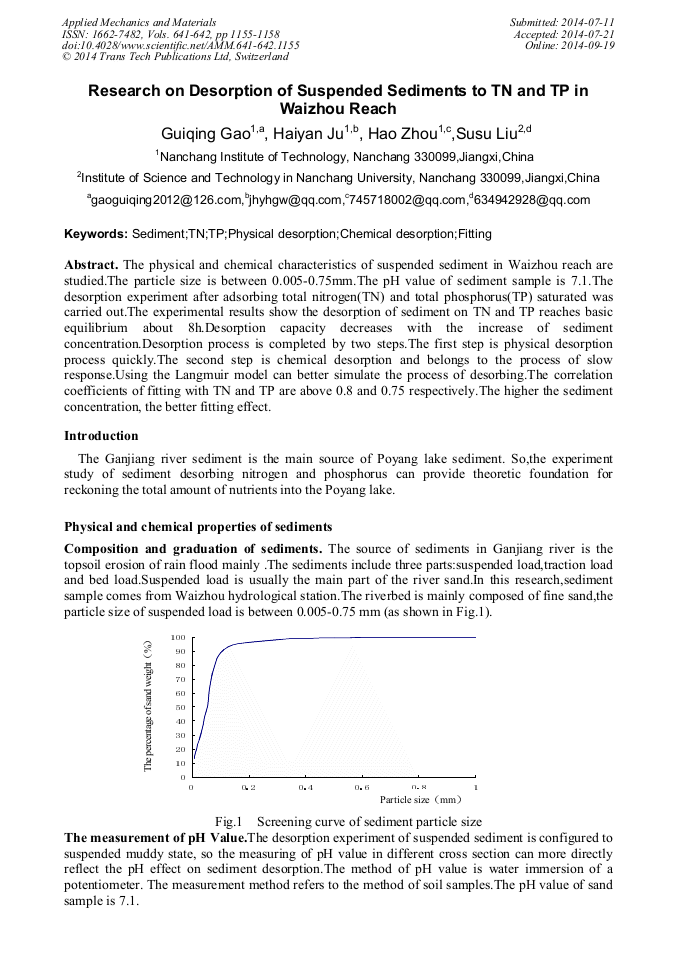
p.1155
p.1159
p.1163
p.1168
p.1172
Research on Desorption of Suspended Sediments to TN and TP in Waizhou Reach
Abstract:
The physical and chemical characteristics of suspended sediment in Waizhou reach are studied.The particle size is between 0.005-0.75mm.The pH value of sediment sample is 7.1.The desorption experiment after adsorbing total nitrogen(TN) and total phosphorus(TP) saturated was carried out.The experimental results show the desorption of sediment on TN and TP reaches basic equilibrium about 8h.Desorption capacity decreases with the increase of sediment concentration.Desorption process is completed by two steps.The first step is physical desorption process quickly.The second step is chemical desorption and belongs to the process of slow response.Using the Langmuir model can better simulate the process of desorbing.The correlation coefficients of fitting with TN and TP are above 0.8 and 0.75 respectively.The higher the sediment concentration, the better fitting effect.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1155-1158
Citation:
Online since:
September 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2014 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: