p.104
p.109
p.113
p.118
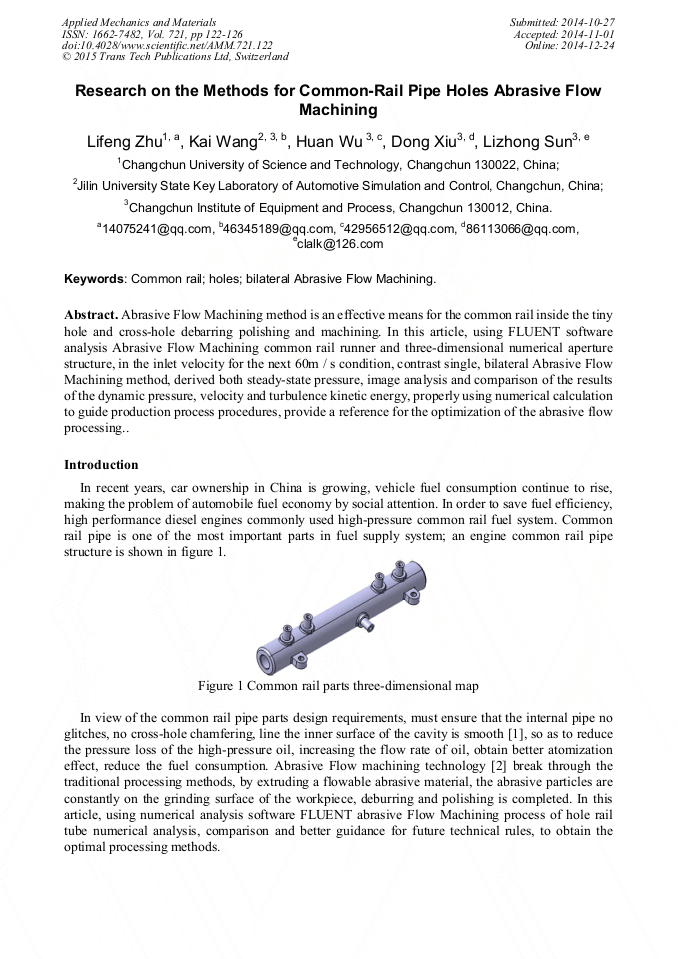
p.122
p.127
p.131
p.135
p.140
Research on the Methods for Common-Rail Pipe Holes Abrasive Flow Machining
Abstract:
Abrasive Flow Machining method is an effective means for the common rail inside the tiny hole and cross-hole debarring polishing and machining. In this article, using FLUENT software analysis Abrasive Flow Machining common rail runner and three-dimensional numerical aperture structure, in the inlet velocity for the next 60m / s condition, contrast single, bilateral Abrasive Flow Machining method, derived both steady-state pressure, image analysis and comparison of the results of the dynamic pressure, velocity and turbulence kinetic energy, properly using numerical calculation to guide production process procedures, provide a reference for the optimization of the abrasive flow processing..
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
122-126
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
December 2014
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2015 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: