p.603
p.609
p.615
p.621
p.627
p.633
p.639
p.645
p.653
Thrust Force Directional Vibration-Assisted Ductile-Mode Grinding of Single-Crystal Si
Abstract:
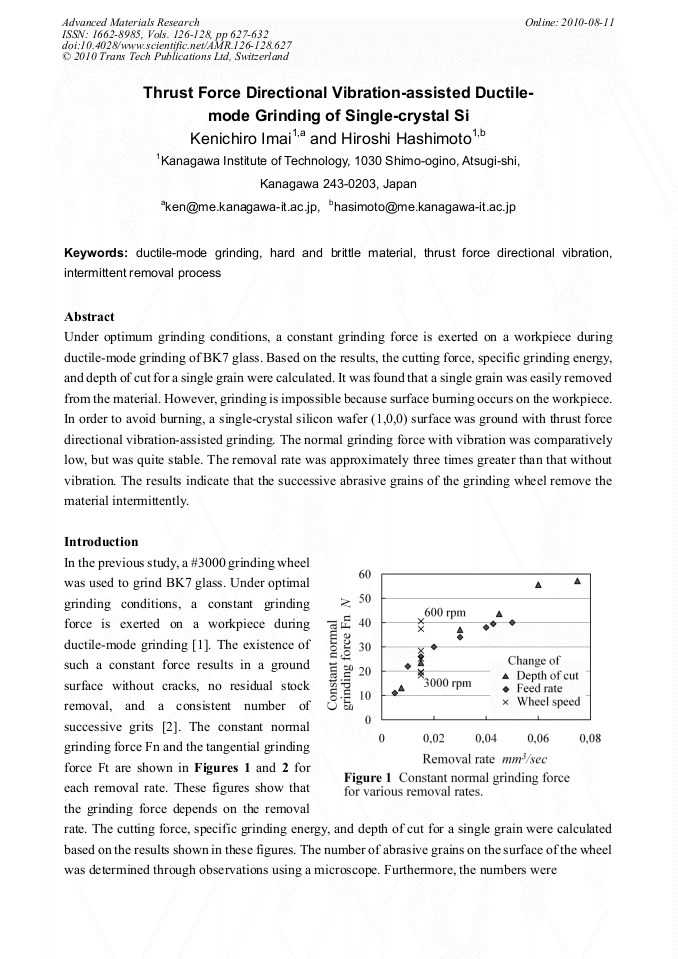
Under optimum grinding conditions, a constant grinding force is exerted on a workpiece during ductile-mode grinding of BK7 glass. Based on the results, the cutting force, specific grinding energy, and depth of cut for a single grain were calculated. It was found that a single grain was easily removed from the material. However, grinding is impossible because surface burning occurs on the workpiece. In order to avoid burning, a single-crystal silicon wafer (1,0,0) surface was ground with thrust force directional vibration-assisted grinding. The normal grinding force with vibration was comparatively low, but was quite stable. The removal rate was approximately three times greater than that without vibration. The results indicate that the successive abrasive grains of the grinding wheel remove the material intermittently.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
627-632
Citation:
Online since:
August 2010
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2010 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: