p.1839
p.1843
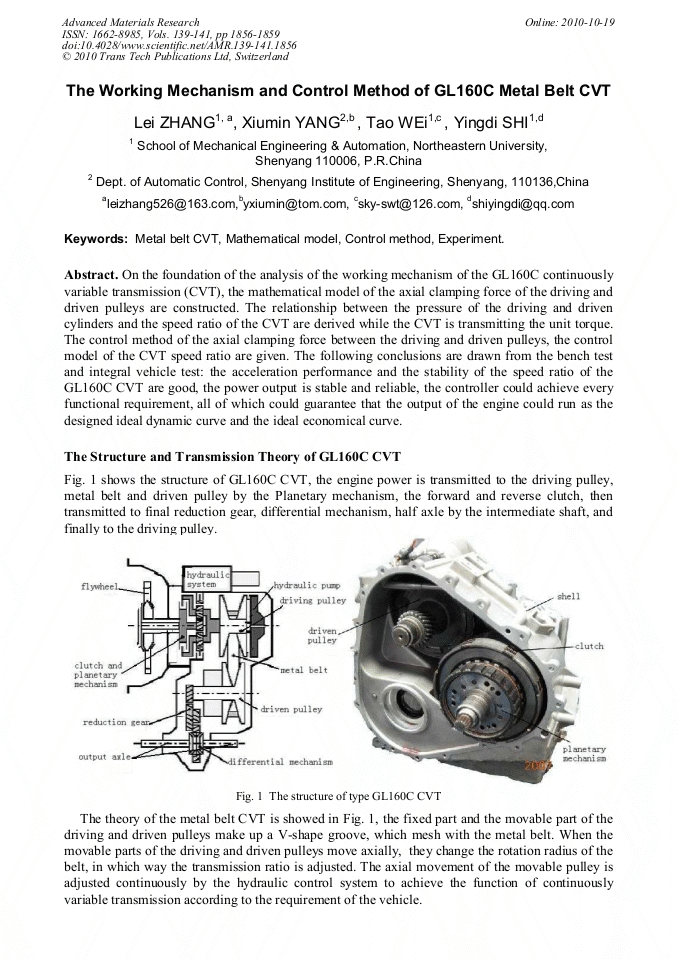
p.1847
p.1852
p.1856
p.1860
p.1864
p.1869
p.1874
The Working Mechanism and Control Method of GL160C Metal Belt CVT
Abstract:
On the foundation of the analysis of the working mechanism of the GL160C continuously variable transmission (CVT), the mathematical model of the axial clamping force of the driving and driven pulleys are constructed. The relationship between the pressure of the driving and driven cylinders and the speed ratio of the CVT are derived while the CVT is transmitting the unit torque. The control method of the axial clamping force between the driving and driven pulleys, the control model of the CVT speed ratio are given. The following conclusions are drawn from the bench test and integral vehicle test: the acceleration performance and the stability of the speed ratio of the GL160C CVT are good, the power output is stable and reliable, the controller could achieve every functional requirement, all of which could guarantee that the output of the engine could run as the designed ideal dynamic curve and the ideal economical curve.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1856-1859
Citation:
Online since:
October 2010
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2010 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: