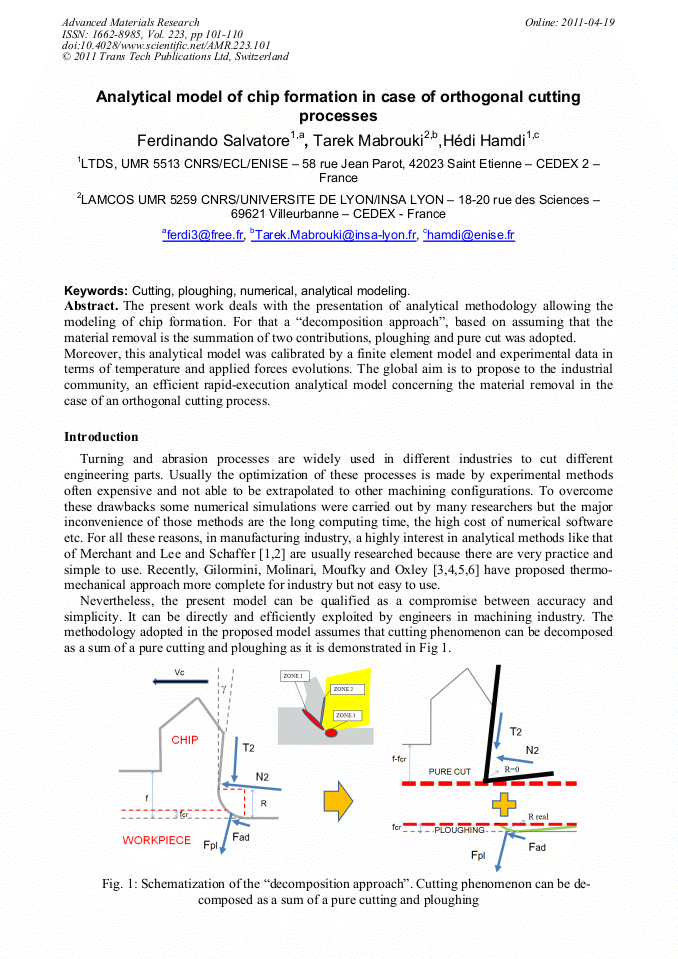
[1]
M.E. Merchant, Mechanics of the metal cutting process. I. Orthogonal cutting and a type 2 chip, Journal of Applied Phys-ics (USA), American Institute of Physics New York. (1945)
DOI: 10.1063/1.1707586
Google Scholar
[2]
E.H. Lee, B.Shaffer, The theory of plasticity applied to problems of machining, Journal of Applied Mechanics, American Society of Mechanical Engineers, New York. pp.405-413. (1951)
Google Scholar
[3]
P.Gilormini, Contribution à la modélisation de la formation du copeau en usinage Phd École des Mines de Paris (1982)
Google Scholar
[4]
A.Molinari, , A new Thermomecanical model of cutting applied to turning operations Part 1 Theory –int- J. Mach. Tools-Manufact 45, 166-180 (2004).
Google Scholar
[5]
A.Moufki, A.Devillez, D.Dudzinski, A.Molinari, , Thermodinamical modeling of cutting and experimental validation, Metal cutting and high speed machining, pp.51-67, (2002)
Google Scholar
[6]
P.L.B. Oxley, Mechanics of machin-ing an analytical approach to assessing machinability, Ellis Horwood limited , Chichester. (1989)
Google Scholar
[7]
M. Barge, Etude expérimentale et numérique des mécanismes de coupe par abrasion". Phd, école centrale de Lyon. (2005)
Google Scholar
[8]
T. Mabrouki, J.F. Rigal, A contribution to a qualitative understanding of thermo-mechanical effects during chip formation in hard turning, journal of material processing technology, n 176 pp.214-221. (2006)
DOI: 10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2006.03.159
Google Scholar
[9]
F.Zemzemi, Caractérisation de modèles de frottement aux interfaces pièce-outils-copeau en usinage: application au cas de l'usinage des aciers et de l'inconel 718, Phd Ecole centrale de Lyon. (2007)
Google Scholar
[10]
F.Salvatore, T.Mabrouki, H.Hamdi, Analytical model of removal material in case of cutting and abrasion processes, Proceedings of the 4th international conference on tribology manufacturing processes. ICTMP, pp.141-150. (2010)
Google Scholar
[11]
V.Pijpanen, Theory of formation of metal chip J Appl. Phys, vol 19, 876-881. (1948)
Google Scholar
[12]
A.Molinari, A. Moufki, The Merchant model of orthogonal cutting revisited: a new insight into the modeling of chip formation. International journal of mechanical science. (2007)
DOI: 10.1016/j.ijmecsci.2007.07.015
Google Scholar
[13]
H.Hamdi, Contribution à l'étude de la physique de l'interface meule-pièce dans le cadre de la rectification conventionnelle et à grande vitesse. Phd, école centrale de Lyon. (2000)
Google Scholar