p.233
p.239
p.246
p.251
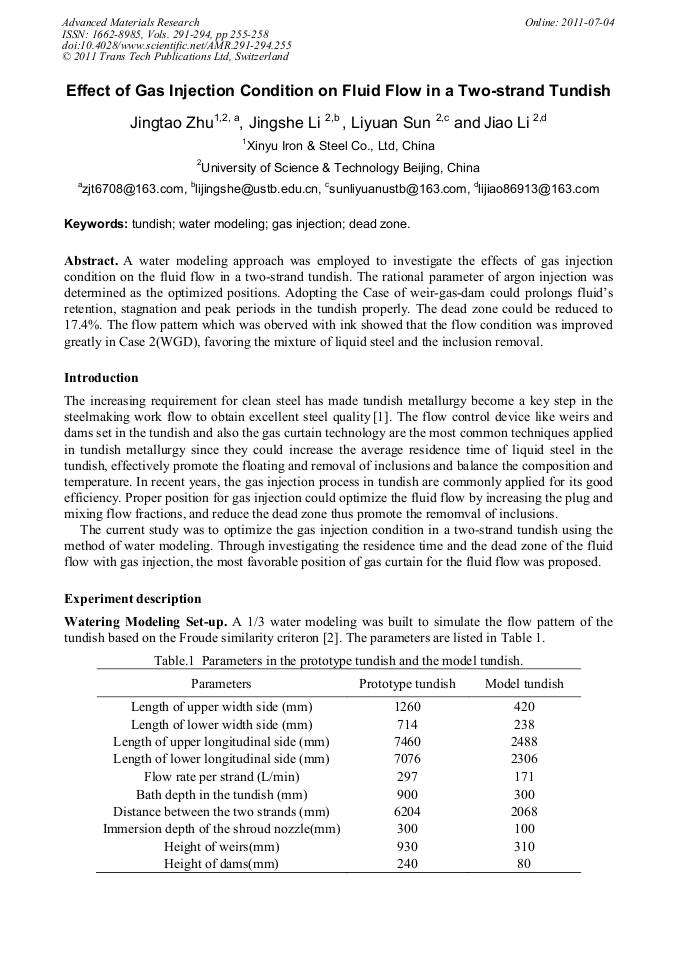
p.255
p.259
p.263
p.269
p.273
Effect of Gas Injection Condition on Fluid Flow in a Two-Strand Tundish
Abstract:
A water modeling approach was employed to investigate the effects of gas injection condition on the fluid flow in a two-strand tundish. The rational parameter of argon injection was determined as the optimized positions. Adopting the Case of weir-gas-dam could prolongs fluid’s retention, stagnation and peak periods in the tundish properly. The dead zone could be reduced to 17.4%. The flow pattern which was oberved with ink showed that the flow condition was improved greatly in Case 2(WGD), favoring the mixture of liquid steel and the inclusion removal.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
255-258
Citation:
Online since:
July 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: