p.682
p.686
p.691
p.695
p.703
p.709
p.713
p.719
p.723
Indirect Hot Stamping of Boron Steel 22MnB5 for an Upper B-Pillar
Abstract:
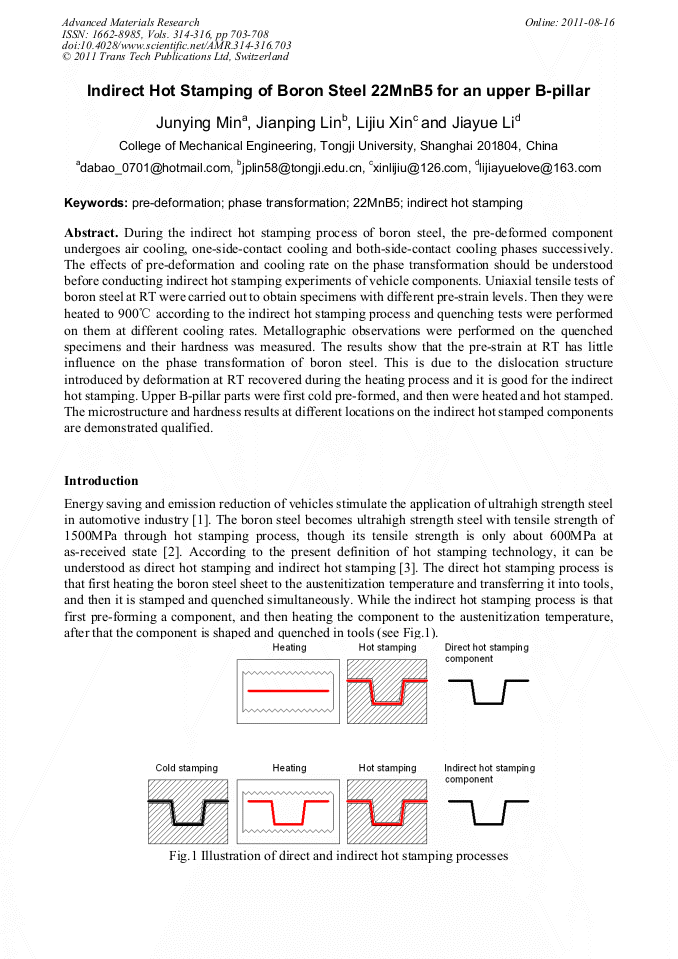
During the indirect hot stamping process of boron steel, the pre-deformed component undergoes air cooling, one-side-contact cooling and both-side-contact cooling phases successively. The effects of pre-deformation and cooling rate on the phase transformation should be understood before conducting indirect hot stamping experiments of vehicle components. Uniaxial tensile tests of boron steel at RT were carried out to obtain specimens with different pre-strain levels. Then they were heated to 900°C according to the indirect hot stamping process and quenching tests were performed on them at different cooling rates. Metallographic observations were performed on the quenched specimens and their hardness was measured. The results show that the pre-strain at RT has little influence on the phase transformation of boron steel. This is due to the dislocation structure introduced by deformation at RT recovered during the heating process and it is good for the indirect hot stamping. Upper B-pillar parts were first cold pre-formed, and then were heated and hot stamped. The microstructure and hardness results at different locations on the indirect hot stamped components are demonstrated qualified.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
703-708
Citation:
Online since:
August 2011
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: