p.33
p.37
p.41
p.46
p.50
p.55
p.59
p.63
p.67
Research on Guiding Strategies of VMS and their Effects Based on Intelligent Materials
Abstract:
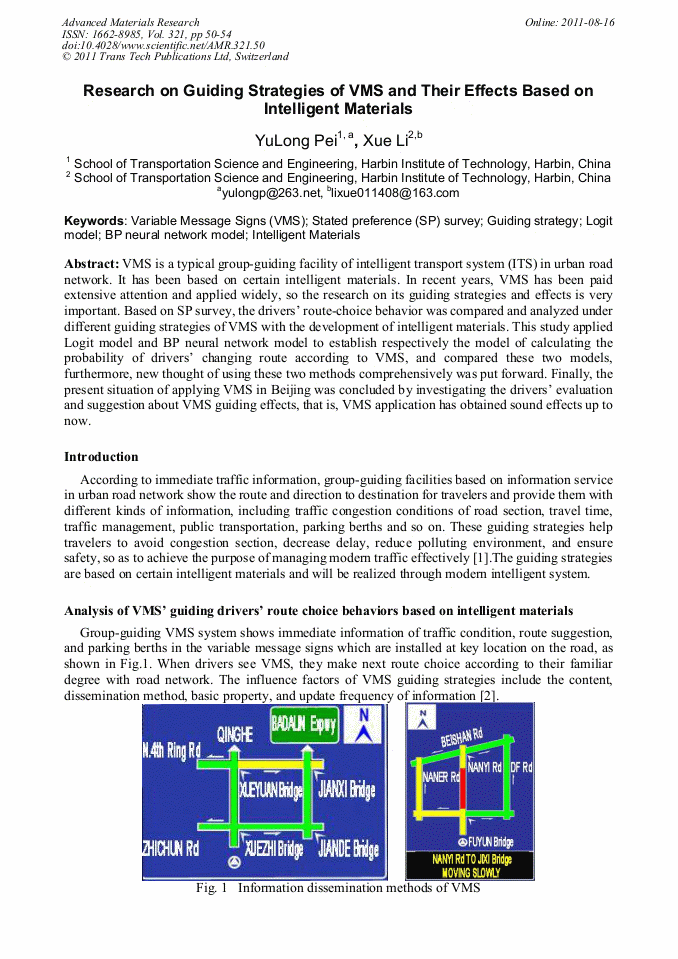
VMS is a typical group-guiding facility of intelligent transport system (ITS) in urban road network. It has been based on certain intelligent materials. In recent years, VMS has been paid extensive attention and applied widely, so the research on its guiding strategies and effects is very important. Based on SP survey, the drivers’ route-choice behavior was compared and analyzed under different guiding strategies of VMS with the development of intelligent materials. This study applied Logit model and BP neural network model to establish respectively the model of calculating the probability of drivers’ changing route according to VMS, and compared these two models, furthermore, new thought of using these two methods comprehensively was put forward. Finally, the present situation of applying VMS in Beijing was concluded by investigating the drivers’ evaluation and suggestion about VMS guiding effects, that is, VMS application has obtained sound effects up to now.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
50-54
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
August 2011
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2011 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: