p.194
p.201
p.209
p.215
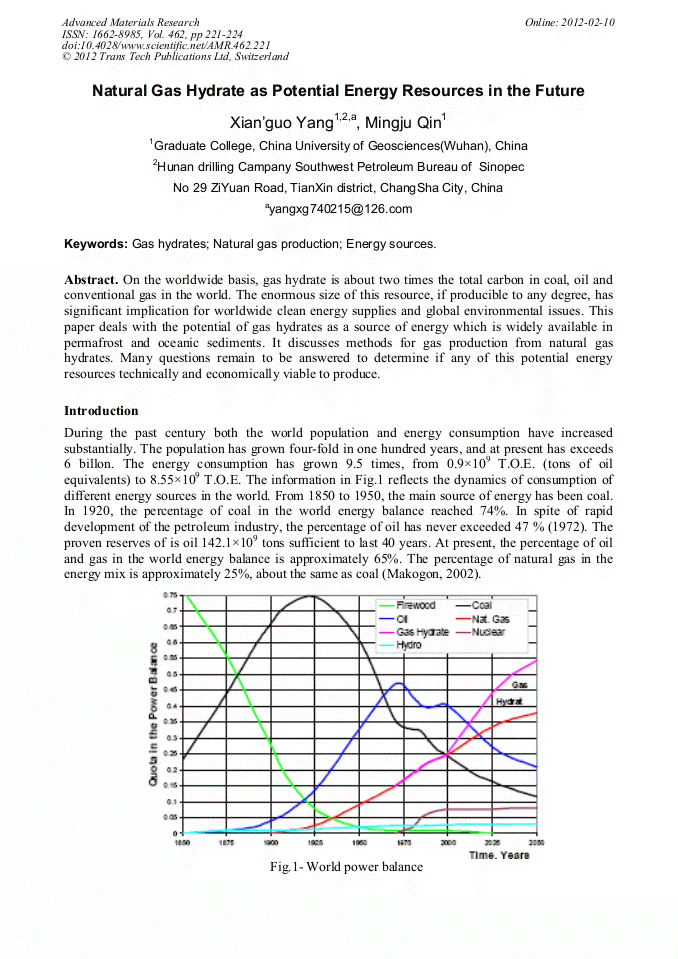
p.221
p.225
p.235
p.242
p.246
Natural Gas Hydrate as Potential Energy Resources in the Future
Abstract:
On the worldwide basis, gas hydrate is about two times the total carbon in coal, oil and conventional gas in the world. The enormous size of this resource, if producible to any degree, has significant implication for worldwide clean energy supplies and global environmental issues. This paper deals with the potential of gas hydrates as a source of energy which is widely available in permafrost and oceanic sediments. It discusses methods for gas production from natural gas hydrates. Many questions remain to be answered to determine if any of this potential energy resources technically and economically viable to produce.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
221-224
DOI:
Citation:
Online since:
February 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: