p.181
p.186
p.191
p.196
p.201
p.207
p.212
p.216
p.220
Rapid Development of New Sanitary Ware Products of Ceramics and Application Study with Computer
Abstract:
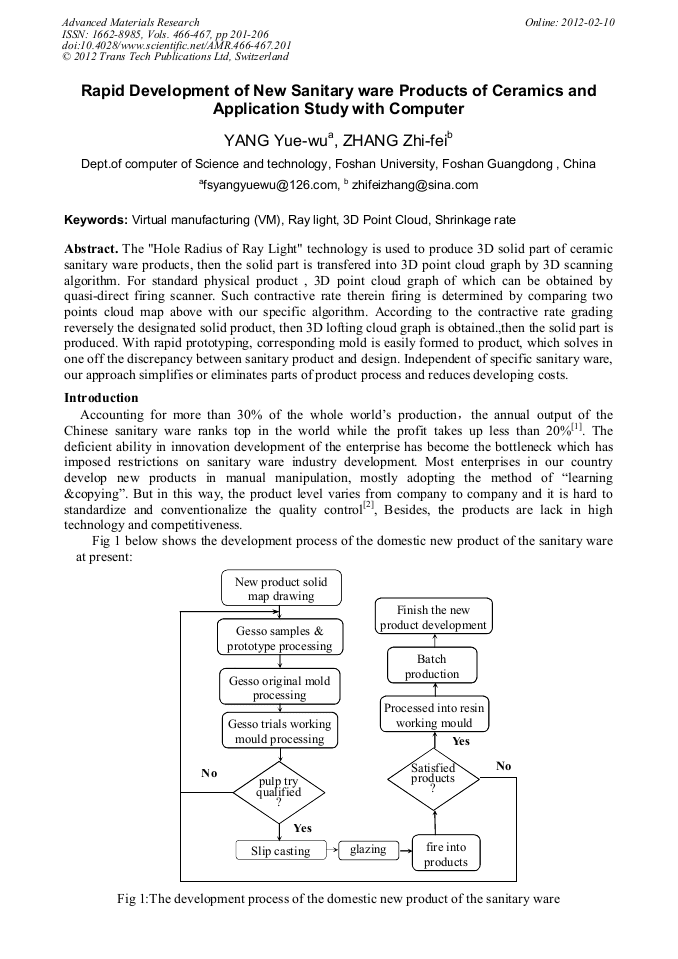
The "Hole Radius of Ray Light" technology is used to produce 3D solid part of ceramic sanitary ware products, then the solid part is transfered into 3D point cloud graph by 3D scanning algorithm. For standard physical product , 3D point cloud graph of which can be obtained by quasi-direct firing scanner. Such contractive rate therein firing is determined by comparing two points cloud map above with our specific algorithm. According to the contractive rate grading reversely the designated solid product, then 3D lofting cloud graph is obtained.,then the solid part is produced. With rapid prototyping, corresponding mold is easily formed to product, which solves in one off the discrepancy between sanitary product and design. Independent of specific sanitary ware, our approach simplifies or eliminates parts of product process and reduces developing costs.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
201-206
Citation:
Online since:
February 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: