p.996
p.1000
p.1004
p.1012
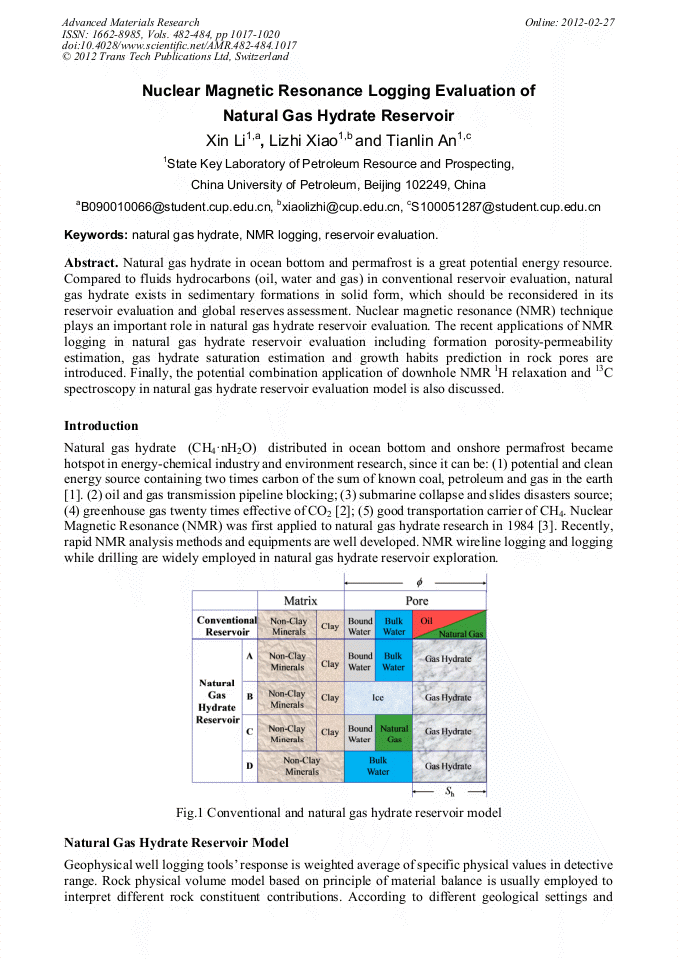
p.1017
p.1021
p.1025
p.1037
p.1041
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Logging Evaluation of Natural Gas Hydrate Reservoir
Abstract:
Natural gas hydrate in ocean bottom and permafrost is a great potential energy resource. Compared to fluids hydrocarbons (oil, water and gas) in conventional reservoir evaluation, natural gas hydrate exists in sedimentary formations in solid form, which should be reconsidered in its reservoir evaluation and global reserves assessment. Nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) technique plays an important role in natural gas hydrate reservoir evaluation. The recent applications of NMR logging in natural gas hydrate reservoir evaluation including formation porosity-permeability estimation, gas hydrate saturation estimation and growth habits prediction in rock pores are introduced. Finally, the potential combination application of downhole NMR 1H relaxation and 13C spectroscopy in natural gas hydrate reservoir evaluation model is also discussed.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
1017-1020
Citation:
Online since:
February 2012
Authors:
Keywords:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: