p.5901
p.5905
p.5909
p.5921
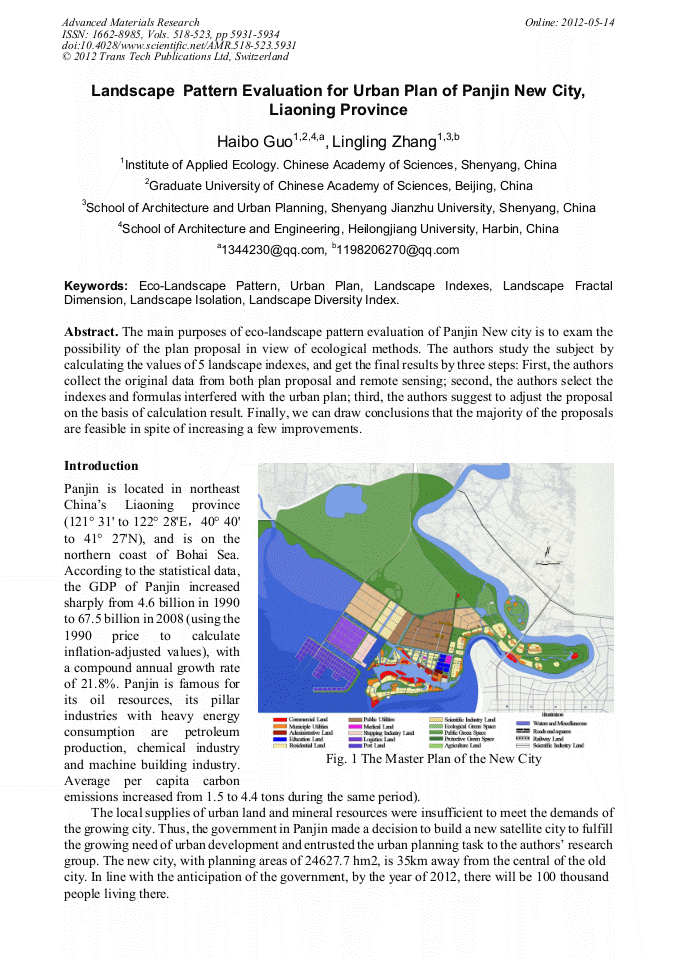
p.5931
p.5935
p.5939
p.5943
p.5949
Landscape Pattern Evaluation for Urban Plan of Panjin New City, Liaoning Province
Abstract:
The main purposes of eco-landscape pattern evaluation of Panjin New city is to exam the possibility of the plan proposal in view of ecological methods. The authors study the subject by calculating the values of 5 landscape indexes, and get the final results by three steps: First, the authors collect the original data from both plan proposal and remote sensing; second, the authors select the indexes and formulas interfered with the urban plan; third, the authors suggest to adjust the proposal on the basis of calculation result. Finally, we can draw conclusions that the majority of the proposals are feasible in spite of increasing a few improvements.
Info:
Periodical:
Pages:
5931-5934
Citation:
Online since:
May 2012
Authors:
Price:
Сopyright:
© 2012 Trans Tech Publications Ltd. All Rights Reserved
Share:
Citation: